Find the terms by letter
Completeness
Definition
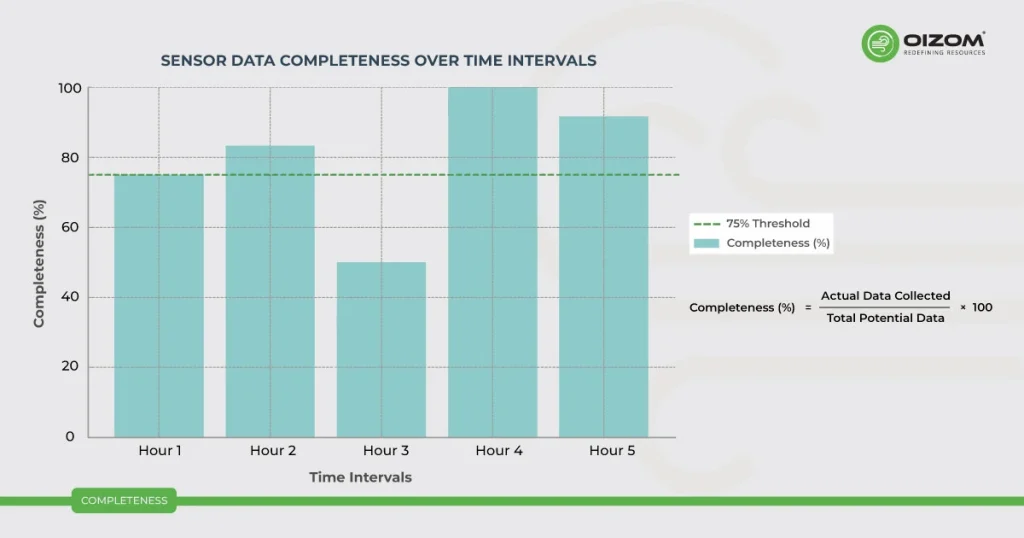
Completeness measures the amount of data a sensor collects compared to the amount of data that was possible to collect if the sensor operated continuously, without data outages, during a period (e.g., 1 hour, 1 day). A 75% completeness level is a useful criterion to meet as the averaged data is generally representative of that time period. For example, at least 45, 1 minute measurements are needed to make a valid 1-hour average at 75% completeness.
Definition and Description
Completeness, in the context of data from a sensor, quantifies the extent to which the sensor’s data collection matches the potential data that could have been gathered if the sensor functioned continuously without any interruptions during a specified time interval (e.g., 1 hour or 1 day). Achieving a 75% completeness level is considered valuable because it typically ensures that the averaged data remains reasonably representative of the designated time frame. To illustrate, meeting this threshold might entail having at least 45 one-minute measurements to produce a valid one-hour average when completeness is at 75%.