Find the terms by letter
EMF (electromotive force)
Definition
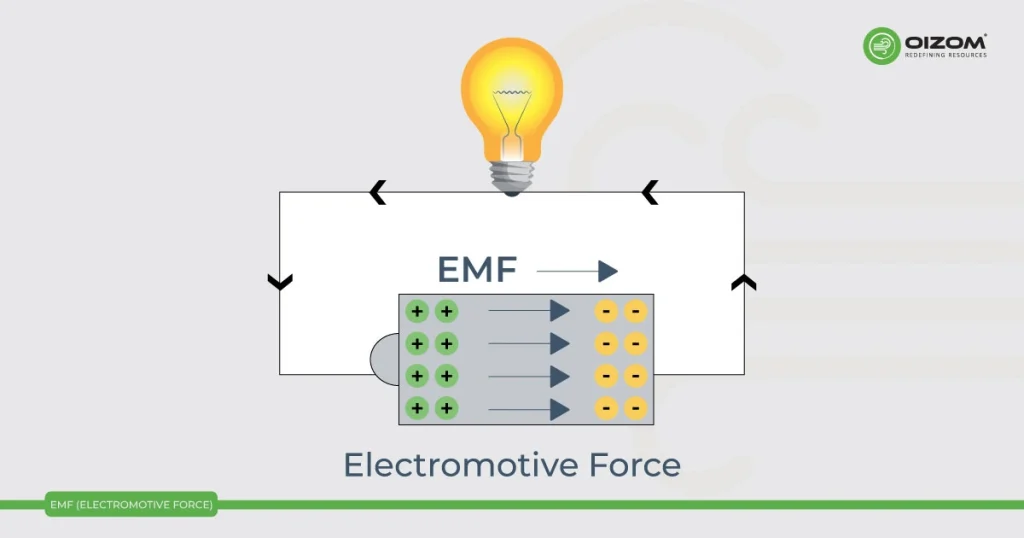
Electromotive Force (EMF) is a concept in physics related to electrical circuits and the potential difference that drives the flow of electric current. Despite its name, EMF is not a force in the mechanical sense but rather an electrical potential difference or voltage. It represents the energy per unit charge supplied by a source, such as a battery or a generator, to move electric charge through a circuit. Strong electromotive force (EMF) disrupts the sensor functioning and generates erroneous results.
Definition and Description
EMF stands for Electromotive Force. It represents the electrical voltage or potential difference generated within a device, such as a battery or a generator, to propel electric current through a circuit. EMF is typically measured in volts (V) and represents the force that pushes electrons through a conductor, creating an electric current. It’s an essential concept in electrical and electronic engineering, as it drives the flow of electricity in various electrical devices and systems.