Find the terms by letter
MAE
Definition
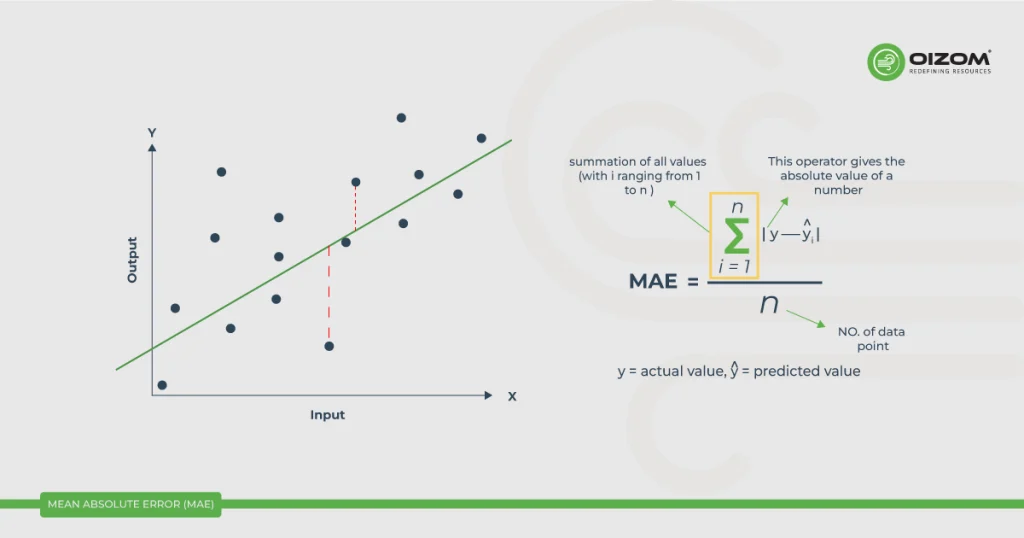
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) is a statistical metric used to measure the average magnitude of errors or inaccuracies between predicted values and actual values in a dataset. It quantifies the absolute differences between individual data points in a predictive model’s output and the corresponding true values. MAE provides a straightforward and easy-to-understand assessment of the model’s accuracy, with smaller MAE values indicating that the model’s predictions are closer to the actual values. MAE is particularly useful in regression and forecasting tasks to evaluate the overall performance of the predictive model.
Definition and Description
MAE stands for “Mean Absolute Error.” It is a commonly used metric in statistics and machine learning to measure the accuracy or performance of a predictive model or estimator, particularly in regression analysis. It quantifies the absolute differences between individual data points in a predictive model’s output and the corresponding true values. MAE quantifies how close the predictions or estimates of a model are to the actual observed values.