Sulfur oxides, a group of gases made of sulfur and oxygen atoms like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and sulfur trioxide (SO3), play a key role in air quality. Among them, sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a major concern for air pollution, as it is released into the atmosphere from various sources, such as burning fossil fuels and industrial processes. Although often invisible, these gases significantly impact both health and the environment, contributing to issues like respiratory problems and acid rain. SO2 is also one of six “criteria pollutants” regulated under the Clean Air Act, which sets national air quality standards to protect public health and the environment.
Monitoring SO2 levels is an effective approach to identifying and preventing exposure to sulfur oxides, lowering hazardous pollutants such as fine sulfate particles, acid rain, and smog. This article will provide a basic overview of sulfur dioxides in the atmosphere, where they come from, the permissible levels in the air, their influence on health and the environment, and why monitoring SO2 is necessary. In addition, we will look at the various working principles for sulfur dioxide monitoring in the ambient environment. Whether you’re concerned about air quality or just curious about the science behind it, this introduction will give you a clear understanding of sulfur dioxides.
1. What is SO2?
- The image is for reference only.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colorless gas with a strong, sharp odour that can cause discomfort, often making it hard to breathe. It is mainly released into the air from burning sulfur-rich fuels like coal, oil, and diesel, especially in power plants and industrial operations like copper smelting. Natural sources, such as volcanic eruptions, also emit SO2. This gas dissolves easily in water and can become a liquid under pressure, contributing to environmental problems like acid rain.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) in the atmosphere reacts with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form sulfuric acid, which can return to the ground through rain, snow, fog, or dry particles in a process called atmospheric deposition. This can harm plants, degrade soil, acidify lakes and streams, and even corrode buildings, statues, and cultural monuments. While SO2 is naturally present in the air, its levels can rise significantly due to volcanic eruptions and human activities like burning fossil fuels. These increased levels can have serious impacts on human health, ecosystems, and the environment.

Sulfur Dioxide is released into the atmosphere by both anthropogenic and natural sources.
- Volcanic eruptions: Volcanic eruptions are one of the natural origins of sulfur oxides. As molten lava rises to the top, the pressure on the magma falls, allowing dissolved sulfur and other volatile components to mix and form a variety of new gasses. Volcanic eruptions release sulfides, which can travel upward into the stratosphere and interact with water particles to form acid rain.
- Fossil fuels, particularly those with a low filtration process, contain a significant concentration of sulfur, which contributes to the generation of several sulfur oxides. The combustion of fossil fuels such as oil, coal, diesel, and other sulfur-containing materials produces sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Industrial facilities are the largest source of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, primarily from burning fuels in power plants and industrial processes like oil extraction and refining. In cities, internal combustion engines, especially diesel engines, contribute significantly to SO2 levels. However, initiatives like the Indian government’s push for BSVI-compliant engines have played a key role in reducing pollution and improving air quality.
- Other Source: Other smaller sources include industrial processes such as extraction of metal from ore, aluminum smelting, refining of oil, pulp mills, and emission from locomotives, ships, and other vehicles and heavy equipment that burn sulfur-containing fuels.
Where do you find the world’s highest SO2 concentrations?
The world’s sulfur dioxide hotspots are:
- In 2022, India emitted approximately 11.2 million metric tons of sulfur dioxide (SO₂), which accounted for roughly 16 percent of global SO₂ emissions that year, making it the world’s biggest emitter of this toxic air pollutant.
- Russia is the second largest emitter of SO2, causing approximately 12% of global emissions. Most of the SO2 emissions stem from smelters (75%), followed by oil and gas (15%) and coal (10%).
- China emitted approximately 8% of global SO2 emissions, mainly from its coal-fired power generation, which has the largest capacity in the world.
SO2 in Atmosphere:
SO2 is naturally present in the atmosphere at very low concentrations. Most of it is caused by human activity, specifically the combustion of fuel, particularly ship fuel, which contains a high proportion of sulfur. Sulfur oxides are found in excess in urban environments. Sulfur dioxide has a life in the atmosphere of less than a week, during which time it combines with other pollutants to generate a variety of chemical compounds.
When SO2 combines with the oxygen present in the environment, it generates sulfur trioxide, which mixes with water vapor and forms sulfuric acid (H2SO4), a primary acid rain component. It can also attach to dust and soot particles in the atmosphere to form particulates. From these reactions, other secondary pollutants, such as smog, are formed, which are extremely hazardous to health and the environment.
3. Permissible Levels of SO2
Below are the breakpoint concentrations describing the quality of air based on sulfur dioxide concentrations for different countries. In India, daily average SO2 levels of up to 80 µg/m3 are considered satisfactory.
Table: Breakpoints of Sulfur Dioxide (µg/m3)
|
India (24-hr) |
US (24-hr) |
China (24-hr) |
EU (8-hr) |
||||
|
AQI Category |
Breakpoint concentration |
AQI Category |
Breakpoint concentration |
AQI Category |
Breakpoint concentration |
AQI Category |
Breakpoint concentration |
|
Good |
40 |
Good |
50 |
Excellent |
89 |
Very low |
50 |
|
Satisfactory |
80 |
Moderate |
150 |
Good |
377 |
Low |
100 |
|
Moderately polluted |
380 |
Unhealthy for sensitive |
475 |
Lightly Polluted |
587 |
Medium |
350 |
|
Poor |
800 |
Unhealthy |
800 |
Moderately Polluted |
797 |
High |
500 |
|
Very Poor |
1600 |
Very Unhealthy |
1600 |
Heavily Polluted |
1583 |
Very high |
500+ |
|
Severe |
1600+ |
Hazardous |
1600+ |
Severely Polluted |
1583+ |
||
[Source: National Ambient Air Quality Index, CPCB (Oct 2014)]
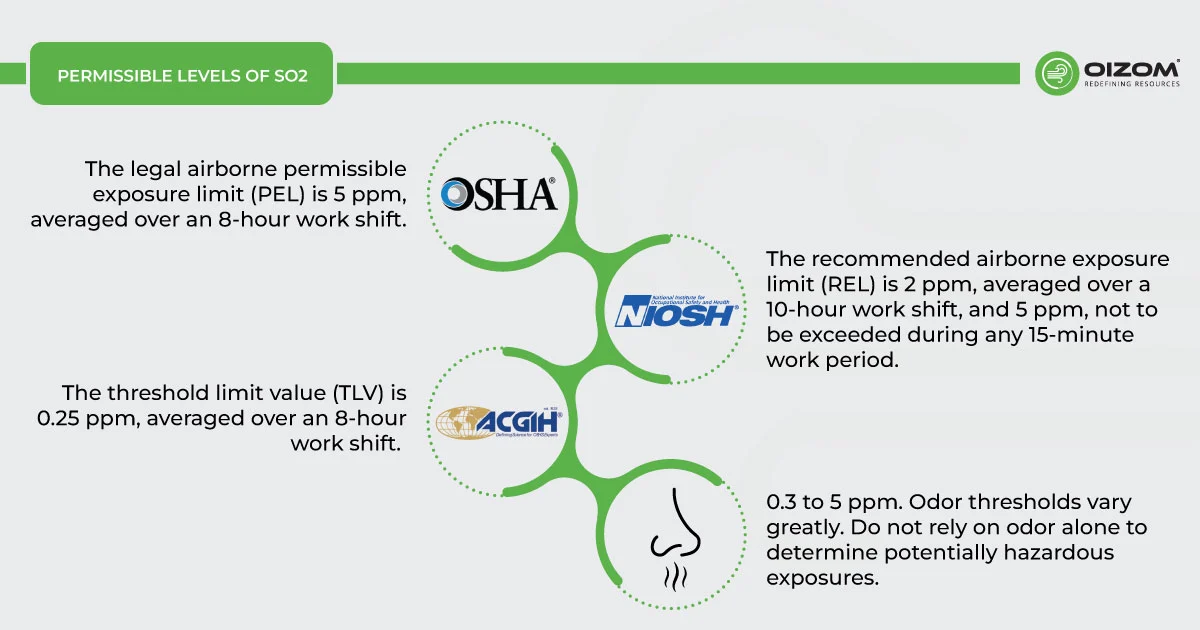
Because sulfur dioxide and other sulfur oxides are emitted in similar ways, these standards have the added benefit of reducing emissions of other SOx as well. Here, you can find workplace exposure limits as well:
- Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA): The legal airborne permissible exposure limit (PEL) is 5 ppm, averaged over an 8-hour work shift.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH): The recommended airborne exposure limit (REL) is 2 ppm, averaged over a 10-hour work shift, and 5 ppm, not to be exceeded during any 15-minute work period.
- American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH): The threshold limit value (TLV) is 0.25 ppm, averaged over an 8-hour work shift.
- Odour Threshold = 0.3 to 5 ppm. Odour thresholds vary greatly. Do not rely on odour alone to determine potentially hazardous exposures.
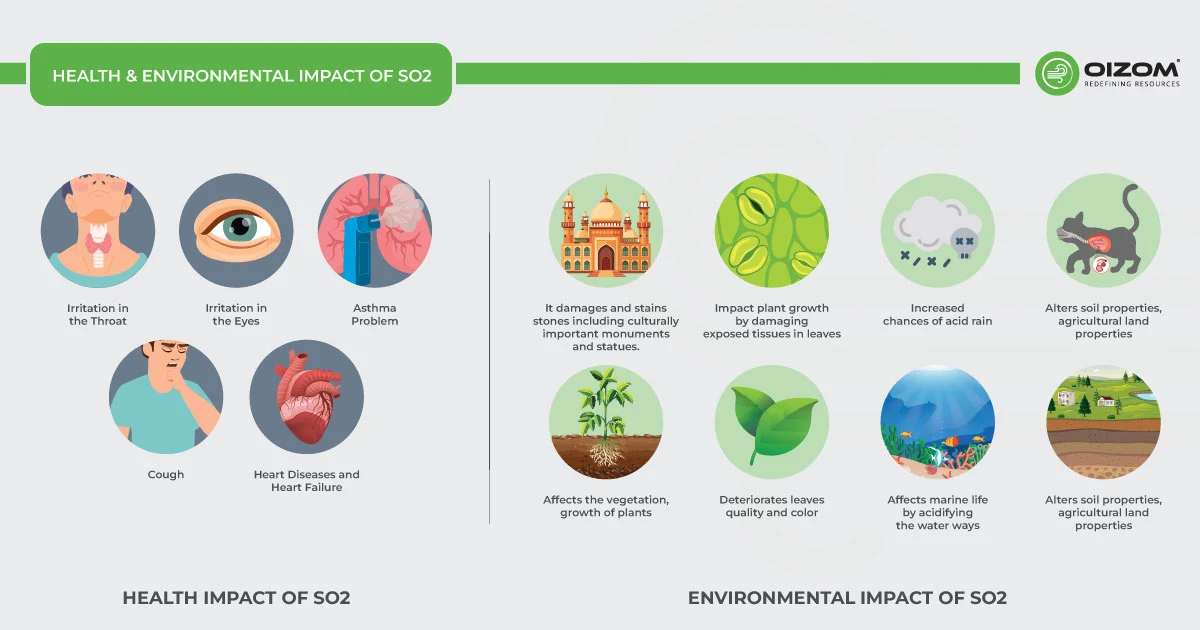
4. Health & Environmental Impact of SO2
Health Impact
SO2, whether volcanic or anthropogenic in origin, is a poisonous gas that, when present in large quantities in the environment, affects air quality and has a major influence on the population’s respiratory and cardiovascular health, even far from the source of emissions. If there is a high concentration of SO2, you can easily inhale SO2, which eventually sticks to the membrane of the nose and respiratory tract.
Even short-term exposure to high sulfur dioxide concentrations irritates the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, and throat. When it enters the respiratory tract, it causes mucus production and coughing. It can irritate the airways and make breathing difficult, causing chronic conditions like bronchitis and exacerbating asthmatic symptoms due to bronchial congestion. People with asthma, the elderly, and children are even more sensitive to SO2 exposures.
At the technical level, engineers and environmental scientists are particularly concerned with SO2 control and management. Technologies and methods for measuring and reducing emissions of this hazardous chemical must be implemented.
Environmental Impact
SO2 has a direct negative impact on the natural environment. It slows down plant growth and destroys leaves, causing them to turn yellow. At high concentrations, it reacts with atmospheric moisture to form an acidic molecule that causes acid rain and damages soil characteristics.
SO2 present in the atmosphere can mix with moisture and other chemicals in the air, forming acids, which fall to the earth as acid rain.
Acid rain can harm sensitive ecosystems:
- It can cause direct harm to trees and plants by damaging exposed tissues and, subsequently, decreasing plant growth
- It affects aquatic ecosystems such as streams and lakes, turning them acidic and toxic to aquatic life.
- It changes the makeup of the soil, affecting its quality and fertility.
Particulate matter formed in the atmosphere due to SO2 emissions, when inhaled, can penetrate deeply into the lungs and, in sufficient quantities, can cause severe health problems, including damaging the lungs, heart, and even the brain. The deposition of these particles can also stain and damage stone and other materials, including culturally important objects such as statues and monuments. Additionally, the sulfate-containing particles can contribute to the formation of smog and thick haze that reduces visibility and impacts health.
5. Possible Corrective Measures
To find solutions that include SO2 concentration, we must first monitor it and identify regions where it does not reach the recommended limits. After determining the target areas, some of the following corrective measures can be implemented:
- Promote using alternative renewable energy such as solar, wind, or hydro to produce power.
- Promote the use of alternative fuels, i.e., fuels with lower or no sulfur content. This will help reduce emissions from burning fossil fuels, which emit SO2. Air pollution can be reduced substantially when we use alternative fuels.
- Avoid living in areas near industrial sites and coal-based power plants. especially sensitive groups that live near industrial areas.
- Also, avoid physical activity outside when pollution levels are high, especially on hot days. Stay indoors until it cools down outside and the air is fresh.
- Using zero-sulfur fuels in cars and other vehicles will help reduce ambient air pollution. Reducing sulfur fuels will also help reduce tailpipe HC, CO, and NOx emissions.
- Installation of power plants with scrubbers: The smokestack scrubber captures hazardous pollutants and chemicals before releasing clean air into the atmosphere through the chimney.
6. Measurement Methods of SO2 Monitoring
Different working principles for sulfur oxide monitoring in the ambient environment are U.V. fluorescence, semiconductor, and electrochemistry.
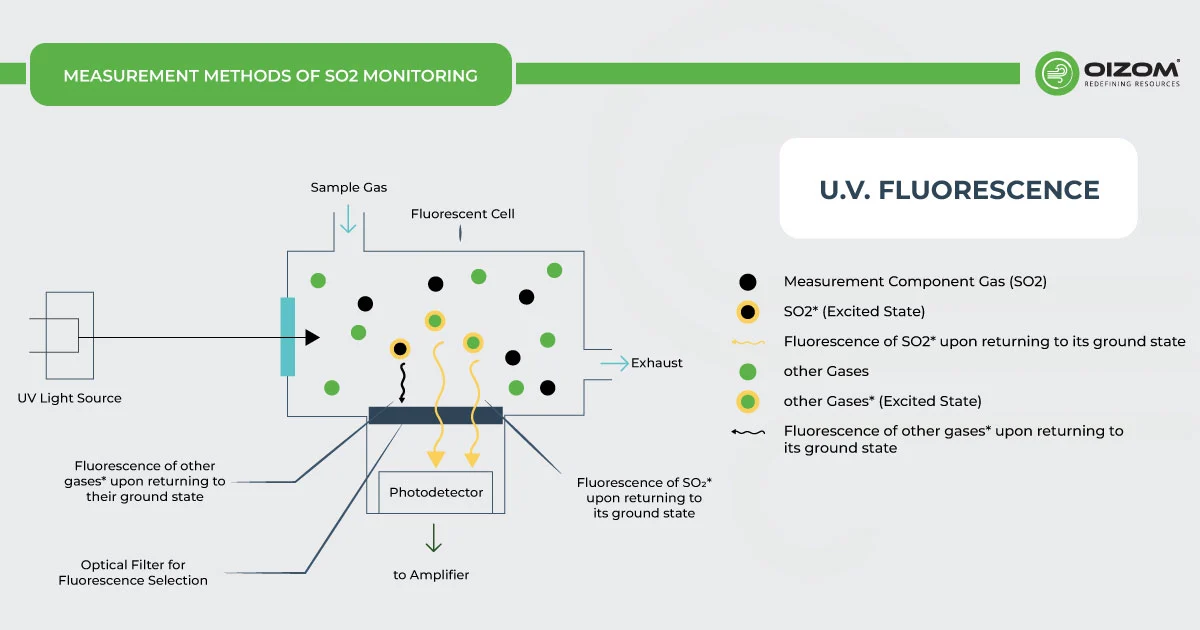
U.V. Fluorescence – The SO2 monitor working on UV fluorescence is based on the emission of a characteristic fluorescence when SO2 molecules are irradiated by U.V. light. When the air sample taken by the SO2 monitor is exposed to the beam of U.V. radiation in the region of 190-230 nm, SO2 gas present in the sample gets excited by the absorption of this light. They emit a characteristic fluorescence radiation of 320-390 nm when they return to their ground state, which is passed through a filter that only allows the radiation of this particular wavelength to pass through and is recorded by the detector (photomultiplier tube) in order to output an SO2 voltage response, which can be scaled into appropriate units of measurement, for example, parts per billion (ppb). The higher the SO2 concentration in the air sample, the greater the fluorescence will be. This method for SO2 monitoring is the most widely used principle in analyzers.
Semiconductor – When a metal oxide semiconductor-based sulfur dioxide monitor is exposed to an air sample, the SO2 molecules react on the metal oxide surface of the sensor and dissociate into charged ions that alter the resistance of the film. This interaction is measured as a signal and is converted to the gas concentration. However, the energy consumption is higher compared to other SO2 monitors.
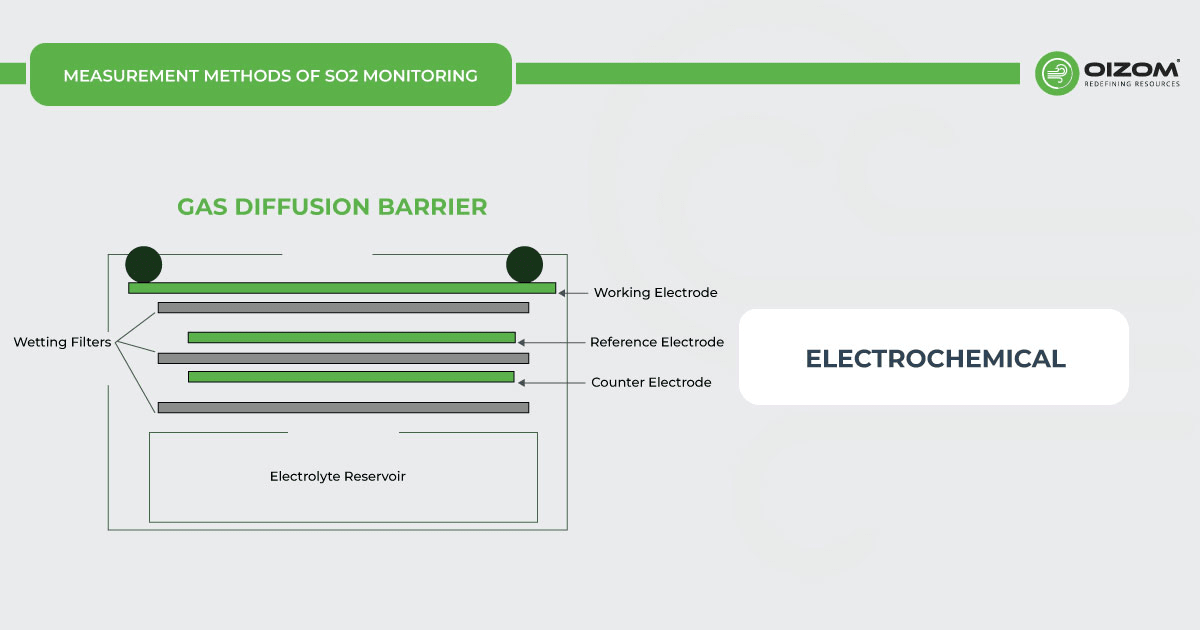
Electro-chemical- SO2 monitors working on the electrochemical principle are operated based on the diffusion of sulfur dioxide gas into the sensor, which results in the production of an electrical signal proportional to the SO2 concentration. It allows accurate measurement of even low concentrations of sulfur dioxide, which is essential in SO2 monitoring in the ambient air.
[Source: iSCAPE Sensors Documentation]
7. Oizom’s Sensor Working Principle for SO2 Monitoring
Oizom provides a range of sulfur dioxide (SO2) sensor modules to monitor varying SO2 levels based on your needs. Our sensors accurately measure SO2 in ambient conditions, detecting concentrations in ppb/ppm. This sensor monitors sulfur dioxide in real time. This sensor is integrated into a metal casing and ultra-low-noise support electronics, making it compact and reliable. This allows accurate gas detection even at very low concentrations in the atmosphere. This sensor works on the Electrochemical working principle to measure environmental air quality.
This sensor undergoes calibration using standard gases and tools to ensure high sensitivity and accuracy. Each gas sensor is calibrated with zero and span checks in a controlled lab, following Section 12.2 of the USEPA Quality Assurance Handbook for Air Pollution Measurement Systems Volume II. Calibration is done using NIST-traceable gas standards for reliable performance.
The SO2 sensor module is integrated into outdoor air quality monitoring systems like Polludrone, AQBot, and Odosense. It is ideal for applications such as campus monitoring, smart cities, industries, wastewater treatment plants, roads, research projects, and environmental impact assessments. By utilizing this sensor module, users can ensure they receive accurate, real-time data on SO2 levels, aiding in the effective monitoring and management of air quality across diverse environments.
8. Why to Choose Oizom SO2 Sensor?
- Compact: Our sensors are small and easy to install, perfect for use in any space, making them ideal for portable air quality monitoring. The SO2 sensors come pre-calibrated and can be quickly replaced in just a few minutes by removing and replacing the old sensor with a new one.
- Durable: The SO2 sensor has a long life of almost two years.
- Energy Efficient: There is no need to be concerned about energy usage because our sensors are not only accurate but also energy efficient. Powered up with just 3.3 to 5V for efficient, reliable performance!
- In-house sensor tech: Oizom applies advanced data processing algorithms to compensate for the effects of temperature and humidity on the sensor output. The algorithm is designed to automatically update based on weather conditions and seasonal changes, removing its influence on the sensor performance. The advanced algorithms also compensate for the effect of the cross-sensitive gas.
- Ultra-Low Noise Electronics: The sensor module’s design is crucial for accurate measurements. Each sensor is housed in a metal casing with ultra-low-noise electronics and a base PCB. The metal casing shields the sensor and electronics from electromagnetic interference, preventing false readings.
- RoHS Compliant: Our sensors comply with the RoHS criteria for restricting hazardous substances in electrical and electronic devices.
9. 5 Reasons Why SO2 Monitoring is Important
- Sulfur dioxide is one of the critical air pollutants produced from the combustion of sulfur-containing fuels. It is majorly emitted from coal-based energy production, resulting in poor air quality.
- The environment is put at a huge risk when exposed to acid rain, which causes deforestation, acidification of water sources, damage to aquatic life, and building corrosion.
- SO2 is a precursor of other sulfur oxides, such as SO3, and many secondary air pollutants, including particulate matter, smog, acid rain, etc., which negatively impact human health and the environment.
- Exposure to high levels of SO2 can lead to long-term effects on the respiratory system, especially in children, the elderly, and people already suffering from respiratory issues.
- Given the serious consequences for human health and the environment, monitoring sulfur dioxide is critical. By monitoring harmful gas levels, we can determine when they are dangerously high.
- Real-time monitoring of SO2 levels helps calculate the air quality index, which delivers health advisories and formulates an action plan to meet standards.
10. FAQs
Is sulfur dioxide flammable?
Sulfur Dioxide itself does not burn. POISONOUS GASES ARE PRODUCED IN FIRE, including Sulfur Oxides. It doesn’t burn or sustain a flame and can be a fire retardant in certain situations.
How does sulfur dioxide affect the environment?
When sulfur dioxide reacts with water and air, it produces sulfuric acid, the primary component of acid rain. Acid rain has the potential to induce deforestation. Acidification of streams harms aquatic life.
Where does sulfur dioxide come from?
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is primarily produced from the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil in power plants and industrial processes. It can also be released during volcanic eruptions and from certain chemical reactions involving sulfur-containing materials.
What is SO2 in air quality?
SO2, in terms of air quality, refers to sulfur dioxide, which is a harmful gas present in the atmosphere. It is one of the key pollutants monitored to assess air quality and its impact on human health and the environment.
What is the full form of SO2?
The full form of SO2 is “Sulfur Dioxide.” It is a chemical compound comprising one sulfur atom and two oxygen atoms, represented by the molecular formula SO2.