Find the terms by letter
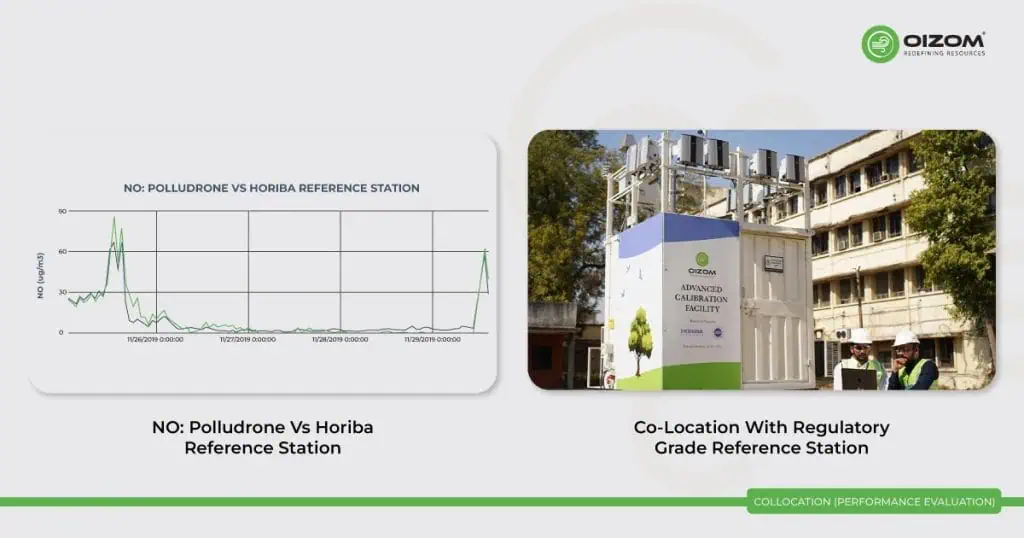
Collocation (Performance evaluation)
Definition
Collocation is the process of checking the performance of an air sensor by installing and operating a sensor in close proximity to a reference instrument(s). The process by which a sensor and a reference instrument are operated at the same time and place under real world conditions. The siting criteria (e.g., proximity and height of the sensor and the reference monitor) should follow procedures outlined in 40 CFR Part 58 as closely as possible. For example, sensors should be placed within 20 meters horizontal of the reference instrument, positioned such that the sample air inlets for the sensors are within a height of ± 1 meter vertically of the sample air inlets of the reference instrument, and placed as far as possible from any obstructions (e.g., trees, walls) to minimize spatial and wind turbulence effects on sample collection.
Definition and Description
Collocation is the practice of evaluating the performance of an air sensor by setting it up and operating it in close proximity to a reference instrument or instruments. This process involves running the sensor and the reference instrument simultaneously and in the same location under real-world conditions. To ensure accuracy, the placement of the sensor should adhere as closely as possible to the specified criteria, such as being within 20 meters horizontally from the reference instrument and aligning the sample air inlets of both instruments within a vertical range of ± 1 meter. Additionally, efforts should be made to position them away from any obstructions like trees or walls to minimize spatial and wind-related disturbances in the collection of air samples.