Find the terms by letter
GHG
Definition
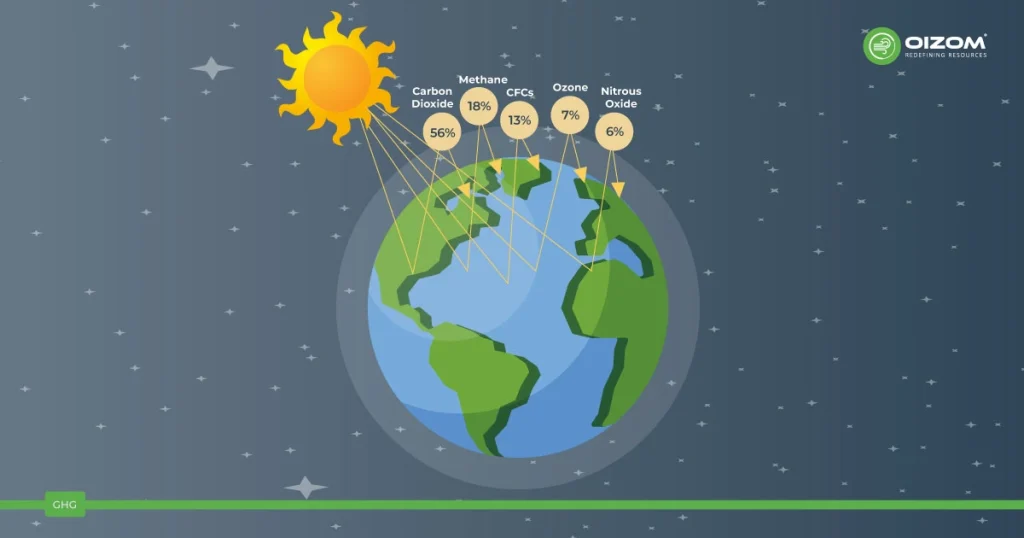
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases present in the Earth’s atmosphere that have the property of trapping heat (infrared radiation) from the sun and preventing it from escaping back into space. This process, known as the greenhouse effect, is essential for maintaining the planet’s temperature within a range that is suitable for life. However, an excess of greenhouse gases can enhance this effect, leading to global warming and climate change. (example – Water vapor (H2O), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous oxide (N2O), Ozone (O3), Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs and HCFCs), Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), Perfluorocarbons (CF4, C2F6, etc.), SF6, and NF3)
Definition and Description
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are atmospheric gases that possess the capacity to trap heat, specifically infrared radiation, from the sun, thereby impeding its release back into space. This natural process, termed the greenhouse effect, is crucial for regulating the Earth’s temperature within a suitable range for sustaining life. However, an excess of these gases can intensify the greenhouse effect, resulting in global warming and alterations in the planet’s climate. Some examples of greenhouse gases include water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs and HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (CF4, C2F6, etc.), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3).