10 Key Takeaway Points:
- Understanding PR: The Performance Ratio (PR) measures how efficiently a solar PV plant converts sunlight into electricity, accounting for real-world conditions.
- Ideal PR Range: A PR between 75% and 80% typically indicates an efficient solar system, though it varies based on location, design, and technology.
- Importance of PR: Monitoring PR helps assess system performance over time, identify issues, and optimize energy output for better returns.
- Oizom Weathercom Role: Devices like the Oizom Weathercom provide accurate solar irradiation, temperature, and humidity data, which is essential for optimizing PR.
- Factors Influencing PR: PR is affected by shading, temperature, solar irradiation, and system losses, impacting the plant’s overall efficiency.
- Calculating PR: PR is calculated using the formula: (Actual Energy Output / Theoretical Maximum Energy Output) x 100%.
- Environmental Impact: Temperature fluctuations and shading can lower PR, while colder modules under full sunlight tend to perform better.
- Maintenance Matters: Regular panel cleaning, wiring checks, and monitoring system health is critical for maintaining a high PR.
- Improving PR: Optimizing panel orientation, using quality components, and avoiding shading can significantly enhance PR.
- Long-term Viability: A high PR contributes to the reliability, economic viability, and sustainability of solar installations, making it a crucial metric for stakeholders.
A Beginner’s Guide to Performance Ratio in Solar Power
Imagine your solar power plant as a smoothly running system, with the Performance Ratio (PR) guiding its efficiency. PR measures how well your solar system converts sunlight into electricity, giving insights beyond energy production. PR shows how well your solar system turns sunlight into electricity, going beyond just measuring energy output. It takes into account things like shading, temperature changes, and system losses, offering a realistic view of how your plant performs.
This contributes to a better knowledge of real-world performance beyond ideal conditions. A high PR indicates the system is performing close to its full capability, whereas a low PR may indicate underlying difficulties. Monitoring the PR allows solar plant owners and operators to promptly fix any performance issues, maximizing energy output and returns on investment. Understanding public relations is critical for maximizing the benefits of solar energy, especially as the world shifts toward renewable energy options. This blog will explore why the Performance Ratio (PR) is important, how to calculate it, the key factors that influence it, and practical tips for improving the PR of a solar plant.
Why is the performance ratio important?

The Performance Ratio is one of the most essential factors in determining the efficiency of a PV system. It can be used to track performance over time and compare PV plants supplying the grid in various places worldwide.
Measuring PR at regular intervals does not provide an absolute comparison, but it does allow operators to assess performance and output under the assumption that the plant is operating optimally or is being commissioned. For this reason, we start with a PR value of 100% and proceed backward.
Gathering additional PR values over time enables operators to discover any deviations and implement suitable actions to fight efficiency decreases. It also enables operators to make changes to improve and optimize plants if the PR value does not correspond to other plants.
How is the Performance Ratio Calculated?
To calculate your PV plant’s performance ratio, you’ll need a few important variables. One key factor is the solar radiation specific to your plant’s location. That’s where the Oizom Weathercom comes in. It measures the incident solar irradiation right at your PV plant, giving you the accurate data you need to fine-tune performance.
It also provides real-time, precise data on solar irradiance, temperature, and humidity. With this info, you can better understand how changing weather conditions affect your plant’s output, make smarter adjustments, and keep everything running smoothly throughout the year. Plus, Oizom Weathercom devices are built to handle different environmental conditions, ensuring you always get consistent and reliable measurements.
On the other hand, you need the factor of your PV plant’s modular area and the relative efficiency of your PV modules. There are two methods of measuring/calculating the Performance Ratio of a Solar PV Plant:
- Manual Calculation
- Automatic Calculation
PR = Actual Energy Output(Kwh/year) / Theoretical Maximum Energy Output(Kwh/year) x 100%.
Factors Affecting the Performance Ratio
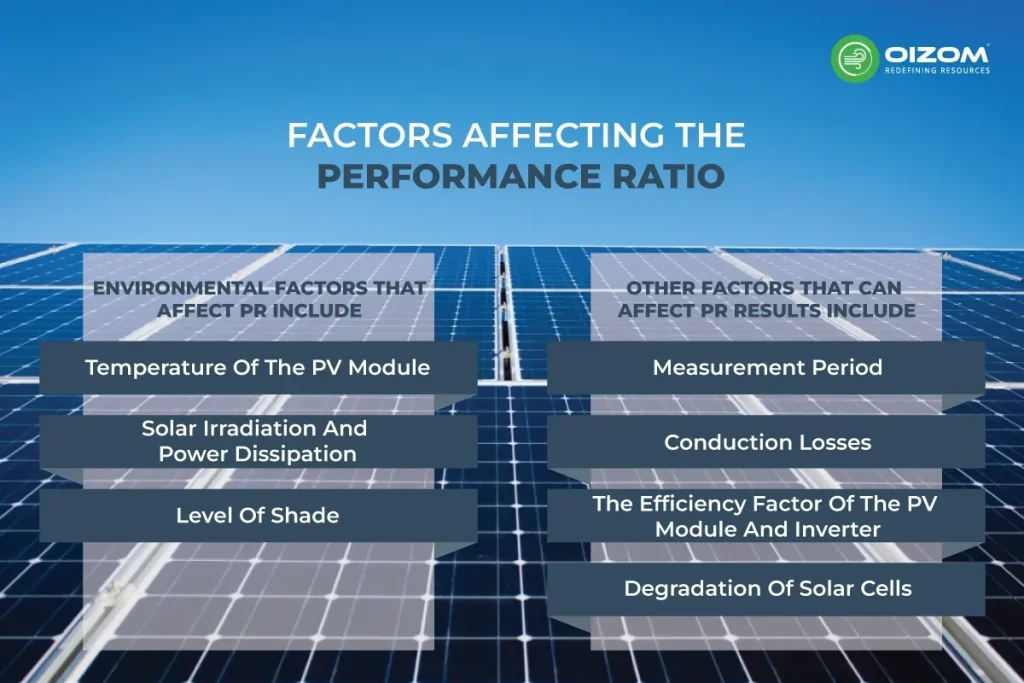
Environmental factors that affect PR include:
- Temperature of the PV module: When the cold PV module receives full solar irradiation, it will perform very efficiently. When the PV module heats up, its efficiency drops again.
- Solar irradiation and power dissipation: The value of incident solar irradiation approaches power dissipation when the sun is low in the sky. PR values will be lower at certain times.
- Level of Shade: If a PV plant’s measurement devices are shaded by surrounding buildings, plants, or even the installation itself, you may get PR readings that are higher than 100%. This can also happen when the measuring instrument gets blocked by snow or dust.
Other factors that can affect PR results include:
- Measurement period: Setting the measurement period too short can lead to incorrect results. To produce a valid PR result, the time frame must be lengthy enough to cover a wide range of conditions.
- Conduction losses: These can arise based on the kind and material of cabling used to transfer electricity from the inverter to the grid operator’s energy export meter. This will reduce the PR value.
- The efficiency factor of the PV module and inverter: The efficiency of your PV modules and inverters will determine your PR value.
- Degradation of solar cells: If you see your PR value declining, it may be a sign that your solar cells are experiencing an age-related decline.
How to Improve the Performance Ratio of a Solar PV Plant
Improving the performance ratio of a solar PV plant is essential for maximizing its energy output and efficiency. Here are some key strategies to consider:
Proper Installation and Orientation:
- Optimal Tilt and Azimuth: Make sure the panels are inclined at the proper angle and facing the right direction to gather the most sunlight throughout the year.
- Shading Avoidance: Reduce shadowing from trees, buildings, and other structures that may block sunlight.
- Quality Components: Use high-quality solar panels, inverters, and other long-lasting components.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning:
- Cleaning Panels: Remove dirt, dust, and debris from the panels regularly to increase their performance.
- Inspecting Wiring and Connections: Look for loose or broken wiring and connections to ensure appropriate operation.
- Monitor System Health: Monitor the system’s performance regularly and address any concerns immediately.
Conclusion
Finally, determining a good performance ratio for solar systems isn’t one-size-fits-all. It depends on factors like location, system design, and technology. Generally, a performance ratio between 75% and 80% is seen as a strong indicator that a solar system is efficiently turning sunlight into electricity. With tools like the Oizom Weathercom device, you can get accurate measurements of solar irradiation, temperature, and other key factors that directly impact your system’s output. This helps you fine-tune your setup for maximum efficiency, boosting energy production and enhancing the overall reliability, economic viability, and sustainability of your solar installation.