- Boost Efficiency: Weather stations optimize solar PV plant performance by providing real-time data on sunlight, wind, and temperature.
- Critical Data: Solar radiation, wind speed, and temperature impact PV output, and monitoring these help improve energy production.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Real-time weather insights support better forecasting, maintenance, and operational adjustments.
- Reduced Costs: Weather data helps in scheduling maintenance and predicting failures, lowering operational costs.
- Increased Energy Yield: Monitoring environmental factors helps enhance long-term energy output and system efficiency.
- Solar Radiation is Key: Pyranometers measure solar irradiance, which is crucial for optimizing PV panel positioning and energy generation.
- Wind and Rain Matter: Wind cools PV modules, improving efficiency, while rain can clean or harm panels, making weather monitoring essential.
- Temperature Sensors: Monitoring air temperature ensures PV panels operate optimally in varying weather conditions.
- Real-Time Alerts: Weather stations provide warnings for high winds or storms, protecting PV systems from damage.
- Smarter Decisions: By integrating weather data, PV plant operators can enhance energy output, reduce downtime, and ensure long-term success.
Why Does Your Solar PV Plant Need a Weather Station?
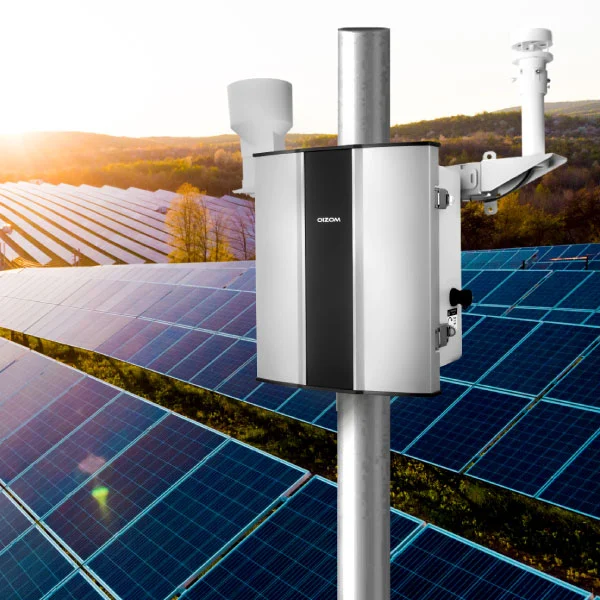
When maximizing the efficiency of a solar PV plant, one of the most essential components is often overlooked: the weather station. A well-equipped weather station does more than just monitor temperature; it provides crucial data that can optimize the performance and lifespan of your solar panels. From monitoring sunlight intensity and wind speed to measuring humidity and precipitation, these stations offer real-time insights that help you make informed decisions about energy production.
In this blog, we’ll look at how a weather station can improve the efficiency of your solar PV plant, what critical characteristics to look for, and how to use this technology for the best results. Whether you manage small or large-scale operations, understanding the purpose of a weather station is critical to getting the most out of your solar investment.
Importance of solar radiation in solar PV systems
One of the most essential considerations when building a solar photovoltaic (PV) system is the amount of sunlight at a potential location.
But why is this so important? Solar energy output can fluctuate based on environmental conditions, and having precise data allows for better forecasting, maintenance planning, and overall management of the plant. By integrating a weather station into your solar PV system, you’re not just collecting data; you’re investing in the long-term success of your energy production.
Weather conditions significantly impact photovoltaic output. Even intermittent cloud cover can significantly impact solar energy. At the same time, other elements such as air temperature, wind direction and speed, precipitation, humidity, and air pressure can all affect solar cell efficiency. Monitoring weather conditions effectively is critical for understanding fluctuations in PV plant performance.
Role of weather stations in optimizing solar PV plant performance
Weather stations play an important role in optimizing the operation of solar PV facilities by providing essential data that directly influences energy production and system efficiency. Here’s how.
Meteorological parameters such as sunshine intensity, temperature, wind speed, and humidity all directly impact how much power a solar PV plant generates. As a result, installing a weather station is critical for accurately predicting and estimating power generation. Weather stations may track and record crucial meteorological data in real-time, including daylight hours, global radiation, temperature, wind speed, and humidity. By gathering this data, the operations team may get insight into daily and seasonal weather patterns, which they can utilize to design more accurate power-generating plans and system maintenance strategies.
- Real-time monitoring and warning: Weather stations come with a range of sensors that enable the real-time monitoring of meteorological data, such as wind speed, wind direction, temperature, humidity, and solar radiation. This information can assist PV staff in staying on top of weather changes and taking the appropriate precautions to avoid potential hazards. For example, when exposed to severe winds or heavy rain, PV panels can be turned off in time to avoid equipment damage and maintenance expenses.
- Improve power generation efficiency: Real-time data from weather stations can also assist PV plant staff in better adjusting equipment operation to boost power generation efficiency. For example, if the strength of solar radiation changes, the angle and orientation of PV panels can be automatically altered to make the best use of sunlight resources. Furthermore, by continuously monitoring climatic data, the PV plant’s power generation pattern may be analyzed to assist in making decisions for future operations and management.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Using the meteorological station’s data, PV power plants can appropriately plan equipment maintenance and overhaul to cut operational expenses. For example, by predicting hot weather in the future, equipment can be examined and cooled ahead of time to avoid failure due to high temperatures. Furthermore, real-time meteorological data monitoring can identify possible safety dangers in time to avoid accidents and lower operational costs.
- Energy Yield Analysis: Weather stations provide essential data for calculating the solar PV plant’s performance ratio (PR), a key indicator of system efficiency. Understanding PR variations due to weather conditions helps optimize Solar power plant operations and improve long-term energy yield.
Components of a Weather Station for Solar PV
A weather station usually consists of the following parts:
Solar irradiance sensor (pyranometer)
Pyranometers measure solar irradiance on flat surfaces in W/m² from a 180° hemispherical view. They are also known as sun irradiance sensors, and they are used in climate research and weather monitoring. However, in recent years, pyranometer use in the solar energy sector has increased.
The global irradiance is the quantity of solar energy per unit area per unit of time derived from both direct and diffuse solar radiation. Direct radiation, also known as direct sunlight, goes from the sun to Earth without being interrupted by clouds or atmospheric particles. Diffuse radiation is sunlight that is scattered by water droplets and air molecules, as well as reflected by buildings, trees, and other objects. Measuring these components is critical for determining the solar energy availability at a specific location. The pyranometer sensor translates global irradiance into a measurable electrical signal.
The pyranometer sensor’s main role is solar monitoring. Solar monitoring measures the amount, intensity, and availability of sunlight. Of course, pyranometers are essential in the solar energy industry. They are vital for evaluating the performance of solar panels and photovoltaic (PV) power facilities. Solar monitoring allows you to improve the location of your solar installation and assess its potential energy yield.
Temperature and Humidity Sensors
- Temperature and humidity sensors are the most basic measurement elements in outdoor weather monitoring. The sensor is used to determine the moisture content of atmospheric humidity.
- Temperature Sensors are used to measure air temperature. Common types include resistance thermometers (RTDs), thermocouples, and semiconductor temperature sensors.
- A temperature sensor is a device that can measure the temperature in the atmosphere. It typically consists of a sensitive element (e.g., thermistor, thermocouple) and a signal processing unit. The sensitive element of the temperature sensor can detect temperature changes in the atmosphere and convert them into an electrical or digital signal, which is subsequently amplified, filtered, linearized, and so on by the signal processing unit, resulting in readable measurement data. Temperature sensors are frequently used in weather stations, satellites, and other weather monitoring systems.
- Humidity Sensor: The two most prevalent types of humidity sensors are capacitive and resistive.
- A humidity sensor is a device that can measure humidity in the atmosphere’s air or water vapor content. It typically consists of a sensitive element (e.g., moisture-sensitive resistor, hygroscopic agents, moisture-sensitive capacitor, piezoelectric elements, etc.) and a signal processing unit. The sensitive element of the humidity sensor detects changes in water vapor content in the atmosphere and converts it into an electrical or digital signal. It then passes through the signal processing unit for amplification, filtering, linearization, and other processing before output as readable measurements.
- Humidity sensors are important for predicting precipitation, cloud formation, and agricultural irrigation.
Wind speed and Direction Sensors
Wind Speed Sensors, also called Anemometers and Wind Direction Sensors, measure the plant’s wind speed and direction and are used to estimate module temperatures. The wind has a substantial impact on PV module temperature. The wind cools PV surface temperatures, which are hotter than ambient air, enhancing their efficiency and output in warm conditions. Wind can also impact soiling, so understanding wind conditions is vital in soil monitoring.
Rain gauge
A sensor for measuring precipitation. Common types include rain gauges, liquid stream gauges, and optical precipitation sensors.A rain gauge is a sensor that measures the amount of precipitation. It properly detects rainfall and assists meteorologists, farmers, and other industry professionals with weather monitoring and water management.
Different types of precipitation can positively and negatively affect PV plants.
- Heavy rainfall can significantly reduce soiling by washing the dirt away. However, moderate rainfall can exacerbate panel soiling. Meanwhile, hail may cause significant damage to panels and equipment.
Data logger and communication system
According to the data logger request, the system generally converts the meteorological data it receives from the sensors into an output signal. Then, it would be sent to the monitoring system. Data can be transferred using analog, Modbus RTU, digital signals, or special communication protocols.
Modern monitors often include data logging and connectivity features. These features can benefit long-term trend analysis, remote monitoring, and integration with other safety systems.
A weather station’s data logger is a device that receives and stores data collected by sensors. It typically has high precision and stability and can process and record data collected by sensors for later analysis and application.
Benefits of Using a Weather Station for a Solar PV Plant
Meteorological sensors allow operators to monitor weather conditions such as wind speed and direction, temperature, humidity, and sun radiation. With this information, they may make better choices about improving the performance of their PV plant.
Furthermore, meteorological stations can assist plant operators in identifying possible difficulties before they escalate into significant ones. For example, if the station detects a decline in solar radiation, it could mean that a panel is faulty or unclean. This data can be utilized to plan maintenance or cleaning, lowering the likelihood of downtime and lost revenue.
The benefits of using meteorological sensors in PV plants must be considered. By providing accurate and real-time data on weather conditions, these sensors can help plant operators optimize the performance of their solar panels, increase efficiency, and ultimately generate more revenue.
Conclusion
Finally, weather stations in solar PV plants are becoming more significant as climate change worsens and PV technology progresses. When faced with more extreme weather circumstances, such as high temperatures, droughts, or strong winds, weather stations enable us to better analyze the tolerance of PV power plants and take appropriate preventive steps. Furthermore, as the size of PV power plants increases, monitoring and management become more involved, and weather stations can give real-time data and reports to help operations teams make precise decisions and optimize plant performance. At Oizom, we know the value of renewable energy and the need for accuracy. That’s why we offer advanced weather and environmental monitoring solutions for solar PV plants, helping you boost performance, optimize energy output, and make smarter decisions in real time.
FAQs
A weather station provides essential data like solar radiation, temperature, and wind speed, helping optimize energy production and ensure efficient system operation.
Delivering real-time weather data enables adjustments to panel positioning, tracks system performance, and helps forecast energy output, leading to increased efficiency.
Weather data is analyzed to adjust operations, plan maintenance, and forecast energy production, ensuring the solar PV plant runs at maximum efficiency under varying conditions.






