Summary
This blog acts as a guide in understanding the importance of the Air Quality Index (AQI). AQI is a crucial tool to understand the pollution levels near us and their potential impact on health. AQI helps people make informed decisions about their daily activities. By checking AQI, we can reduce exposure to harmful pollutants, which can cause long-term health issues, especially in high-pollution areas.
AQI is calculated using pollutant concentrations and break points, for example, PM2.5 levels of 0–12 µg/m³ is “Good” (0–50 AQI), while 55.5–150.4 µg/m³ is considered “Unhealthy” (151–200 AQI). The highest AQI value from pollutants decides the overall AQI. AQI categories differ by country India, the US, EU, and China use similar systems, but breakpoints and reporting standards can different, which makes a “Moderate” AQI in one country different from another.
Real-time AQI apps like AirVisual, Breezometer are resourceful tools that allow users to be aware and protect their health by tracking air quality. By thoroughly interpreting AQI data, individuals can make healthier decisions and reduce their exposure to pollution.
Introduction To AQI
Air Quality Index (AQI) is an important tool for understanding the air quality around us. AQI uses a number scale to show the concentration of pollutants, and the number on the scale represents how polluted the air is and to what extent it will impact our health.
AQI is important in keeping individuals aware and in making informed decisions about their health. High AQI means high pollution levels, which can lead to health risks like respiratory issues, especially for vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and people with prior health issues. For instance, when AQI levels are high, it would be best to reduce outdoor activities or wearing a mask.
Cities like Delhi and Mumbai often make headlines for their high pollution levels, whereas smaller towns like Byrnihat and Begusarai often experience severe deterioration in air quality. This reminds us that air pollution isn’t just an urban problem but something that can affect anyone, anywhere.
To define AQI correctly, it’s important to understand the numbers as well as the associated health risks. Multiple apps offer localized, real-time data, helping users stay informed and take action when needed.
Hence, it is important to be able to interpret AQI like a pro. Mistakes in understanding it could lead to unnecessary risks, especially during times of high pollution. Mastering AQI readings could empower you to protect yourself and those around you, making it important in today’s polluted world.
What is Measured in AQI?
The AQI measures the concentration of various air pollutants that can impact human health. Understanding these pollutants is key to interpreting the AQI and making informed decisions. Here’s an overview of the key pollutants measured in AQI:
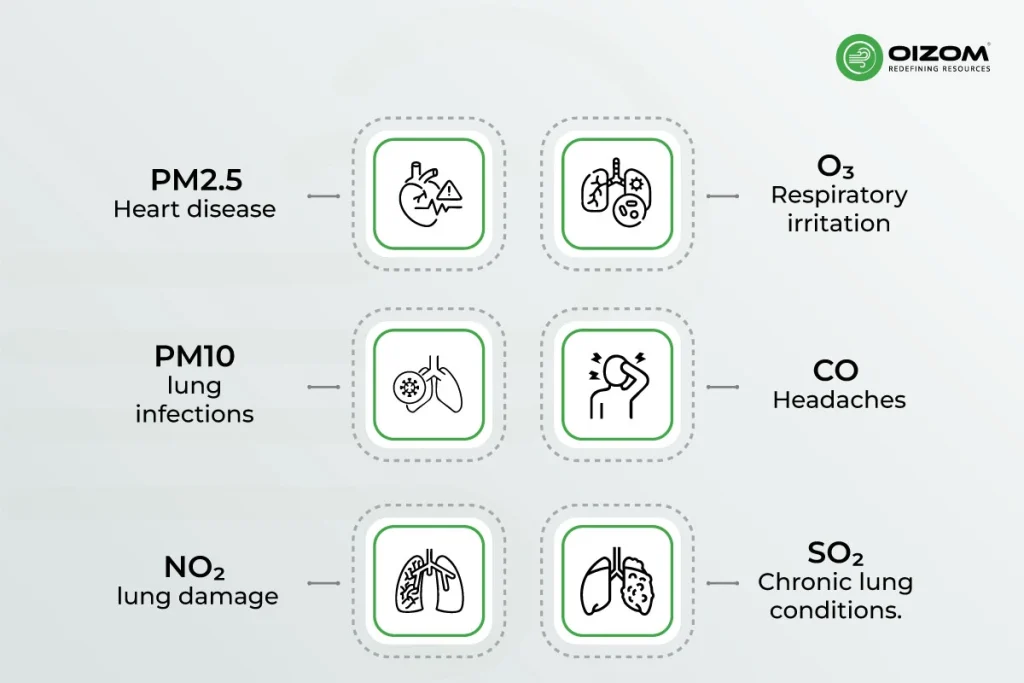
1.PM2.5
These fine particles can enter deep into the lungs, causing respiratory problems, heart disease, and conditions like asthma. PM2.5 is one of the most dangerous pollutants due to its ability to stay in the air for long periods and its small size.
2.PM10
PM10 is larger than PM2.5, but still small enough to be inhaled, it can cause respiratory irritation, lung infections, and worsening of prior conditions like bronchitis, asthma.
3.NO₂ (Nitrogen Dioxide)
It is a major component emitted from vehicular movement. NO₂ can irritate the respiratory system, leading to breathing difficulties, increased asthma attacks, and long-term lung damage if exposure is prolonged.
4.O₃ (Ozone)
Ground-level ozone forms when nitrogen oxides and VOCs react in sunlight. It can cause respiratory irritation, reduce lung function, and increase the risk of respiratory diseases.
5.CO (Carbon Monoxide)
Produced by combustion processes, such as vehicle exhaust and industrial emissions, CO can cause headaches, dizziness, and in large quantities, even lead to unconsciousness or death.
6.SO₂ (Sulfur Dioxide)
Typically emitted by power plants and industrial processes, SO₂ can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and lead to respiratory issues, especially in people with asthma or chronic lung conditions.
Each of these pollutants contributes to the overall AQI, and the numeric value of the pollutant is directly proportional to the level of pollution. Higher AQI numbers indicate worse air quality, which can have serious health implications, especially for sensitive groups like children, the elderly, and those with prior respiratory conditions.
How AQI is Calculated?
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is calculated using a formula that converts the concentration of pollutants into a normalized number. This helps us to easily determine the overall air quality and its impact. Here’s the formula used for AQI calculation:
AQI Formula:
I = ((Ihigh – Ilow) / (Chigh – Clow)) * (C – Clow) + Ilow
Where:
- I = AQI (Air Quality Index)
- C = Concentration of the pollutant (measured in µg/m³ or ppb/ppm)
- Iₗₒₗₗ = Lower breakpoint AQI value
- Iₕᵢᵍʰ = Upper breakpoint AQI value
- Cₗₒₗₗ = Lower breakpoint concentration
- Cₕᵢᵍʰ = Upper breakpoint concentration
Explanation of the Formula:
The AQI formula is designed to convert pollutant concentrations into a numeric score that is easier for the public to understand. Here’s a breakdown of the steps:
1.Finding the Breakpoints
Each pollutant has a range of breakpoints that determine the corresponding AQI categories (like Good, Moderate, Unhealthy). These breakpoints are concentration values that classify air quality and help assess health risks.
2.Apply the Formula
This formula calculates the AQI by reviewing the differences in the concentration of the pollutant to the breakpoints. Here, the difference between the upper and lower breakpoints for both concentration and AQI values is multiplied by the difference between the pollutants and lower concentration breakpoints. The final result is then added to the lower AQI value to give the AQI for that pollutant.
3.Final AQI Calculation
If there are multiple pollutants ( PM2.5, NO₂, CO), the AQI for each pollutant is calculated individually. The peak AQI value from the pollutants is considered the overall AQI, which indicates the worst air quality in the area.
How the Formula Applies to Each Pollutant:
To calculate the AQI for a particular pollutant, apply the formula with the suitable breakpoints and concentration values. In case of multiple pollutants, we need to find the AQI for each one, then choose the highest number to determine the overall AQI.
AQI Breakpoints and Categories
The AQI system has different segments or categories, each representing a range of air quality and related risks. The AQI scale usually ranges from 0 to 500, with higher values representing worsening air quality.
How the AQI Classification System is Structured:
The AQI categories are based on the concentration levels of pollutants. As the concentration of pollutants increases, the AQI number rises. The classification helps you understand if air quality is acceptable or if precautionary steps are needed.
Differences in AQI Classification Across Countries:
- India: In India, AQI classifications focus on pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, and NO₂. The classification is similar to the US and EU, but localized health impacts are also considered, especially in high-pollution regions.
- United States: The US uses the EPA’s AQI standards, where the breakpoints and categories are based on health studies. The classification is generally strict, and a lot of emphasis is placed on short-term exposure to pollutants.
- European Union: The EU has a similar classification system, but the breakpoints can be slightly more lenient compared to the US. In certain areas, the EU may allow higher levels of pollutants in air quality reports.
- China: While China’s AQI system is similar, it’s often reported in terms of a broader range of pollutants. However, surprising to many, some regions in China have significantly improved air quality in recent years, with cities like Beijing seeing improvements due to strict pollution control measures.
Real-World Example: Delhi’s PM2.5 Calculation
AQI Calculation for PM2.5:
The formula we’ll use is:
I = ((Ihigh – Ilow) / (Chigh – Clow)) * (C – Clow) + Ilow
| Concentration (µg/m³) | AQI Range | AQI Category |
|---|---|---|
| 0-12 | 0-50 | Good |
| 13-35.4 | 51- 100 | 51- 100 |
| 35.5- 55.4 | 101- 150 | Unhealthy for Vulnerable Groups |
| 55.5- 150.4 | 151- 200 | Unhealthy |
| 150.5- 250.4 | 201- 300 | Very Unhealthy |
| 250.5- 500 | 301-500 | Hazardous |
Calculation for Delhi’s PM2.5:
Concentration (C) = 160 µg/m³
From the table above, this concentration falls in the Unhealthy category (151 – 200 AQI).
Let’s use the following breakpoints for calculation:
- Iₗₒₗₗ = 151 (lower AQI value for Unhealthy)
- Iₕᵢᵍʰ = 200 (upper AQI value for Unhealthy)
- Cₗₒₗₗ = 55.5 µg/m³ (lower concentration for Unhealthy)
- Cₕᵢᵍʰ = 150.4 µg/m³ (upper concentration for Unhealthy)
Now, we apply the formula:
I = ((Ihigh – Ilow) / (Chigh – Clow)) * (C – Clow) + Ilow
I = ((200 – 151) / (150.4 – 55.5)) * (160 – 55.5) + 151
I = (49 / 94.9) * 104.5 + 151
I ≈ 0.5163 * 104.5 + 151
I ≈ 53.9 + 151
I ≈ 204.9
Final AQI: 204.9
So, the AQI for PM2.5 in Delhi would be approximately 205, which falls into the Unhealthy category.
Why This Matters
Understanding AQI gives everyone a clear and simple glimpse of air quality, helping us make thoughtful decisions in our daily lives. Whether it’s about choosing the best time to go for a walk, determining if it’s safe to exercise outdoors, or knowing when to keep windows closed, AQI plays a crucial role in our health and well-being.
Misunderstanding AQI can lead to unnecessary risks. For example, in cities like Delhi or Mumbai, a “Moderate” AQI may seem safe, but prolonged exposure to even moderate pollution levels can negatively affect lung health. On the other hand, a person might wrongly assume it’s safe to spend long hours outside with a “Good” AQI, unaware of a sudden pollution spike in the forecast. This becomes even more important when unexpected environmental events such as the Potential Impacts of a Tornado on Air Quality can rapidly alter pollutant levels and influence local AQI conditions.
Being a pro at understanding AQI isn’t just about protecting yourself, it’s also about making smarter, healthier decisions for your routine. With the right knowledge, you can minimize exposure to harmful air pollutants and make choices that benefit both your immediate health and long-term well-being.
Apps and websites like AirVisual, Breezometer, and AQICN offer real-time, localized AQI data to keep you informed wherever you are. These tools empower you to track air quality conditions and act accordingly, ensuring that you’re always in the know.
Make it a habit to monitor AQI regularly, whether you’re at home, at work, or out for a run. Understanding the air you breathe is the first step in taking control of your health.
Conclusion
Understanding the Air Quality Index (AQI) is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and well-being. By knowing how AQI works and what it means, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself from harmful pollutants. Whether it’s deciding when to exercise outdoors, keeping windows closed, or adjusting your daily routine, AQI plays a key role in guiding those decisions.
It’s not just about personal safety, regularly checking AQI helps raise awareness of the air quality around us and encourages more conscious actions toward improving environmental health. When more people understand AQI, it leads to collective action and can even inspire changes at the community or governmental level.
Make it a habit to check AQI regularly. Whether you’re planning an outdoor activity, commuting, or simply enjoying time at home, understanding the air quality around you empowers you to make the best choices for your health and the environment. Stay informed, stay safe, and be part of the solution to cleaner air for all.







