Key Takeaways Points:
- Weather Monitors: Weather monitors collect data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and more to predict weather with high accuracy.
- Importance of Weather Monitoring: Reliable weather monitoring is essential for various sectors, aiding in activities like agriculture, aviation, and emergency response.
- Automated Weather Stations (AWS): AWS uses advanced technologies to gather and analyze real-time weather data, which is crucial for both large and small businesses.
- Key Components: A weather monitor consists of sensors, a data logger, data transmission equipment, a power supply system, and a cloud-based platform.
- Weather Sensors: These sensors measure various meteorological parameters, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation, helping in accurate weather prediction.
- Data Logger: The data logger stores sensor data for later analysis, crucial for long-term trend analysis and remote monitoring.
- Data Transmission: Weather data is transmitted via wireless communication modules or network interfaces to central databases for analysis.
- Power Supply Systems: Weather stations use stable power systems, often solar-powered, to function in remote or harsh environments.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Platforms like Oizom’s Envizom offer real-time data acquisition and analysis, providing actionable insights through AI and machine learning.
- Weather Monitoring Networks: Data from ground-based stations, mobile units, and satellites is collected, processed, and shared, forming the backbone of accurate weather forecasting.
How Does a Weather Monitor Work? A Simple Guide
Have you ever wondered how weather forecasts are predicted? Weather monitors play a big role in predicting rain, sunshine, and storms. These devices are collecting data to keep us informed about the weather. Imagine having a personal weather station right in your backyard, constantly measuring temperature, humidity, wind speed, and even rainfall. That’s essentially what a weather monitor does, but on a much larger scale and with far more accuracy.
In this blog, we will explore how this weather monitoring system works, breaking down the science into easy-to-understand bits. From the sensors used to the data they collect, you’ll get a behind-the-scenes look at the technology that helps predict the weather. Whether you’re a researcher, professional, or just curious about how your local forecast is determined, this journey into the world of weather monitors will surely be informative. So, let’s dive in and uncover the magic that turns raw data into the weather predictions we rely on daily.
What is a weather monitor?
Automated weather stations are not just a trend for weather bloggers and enthusiasts. In fact, they are important to many critical activities for both large and small firms. Weather monitoring leverages advanced technologies to offer accurate, real-time data. In a world where weather unpredictability can significantly impact various sectors, having a reliable weather monitoring system is not just beneficial; it’s essential. These smart systems gather and analyze weather data from multiple sensors, providing accurate and timely information to enhance daily life and business operations.
But what exactly is an automatic weather station (AWS)? How do they work? Scroll through this guide to learn more.
Importance of weather monitoring
Measuring and studying the weather has always been important for scientists and farmers, but in recent years, understanding what is going on with the weather has become a growing source of concern around the world. To handle emerging weather concerns, we need devices that can collect data and guide our planning in various situations and scenarios.
Monitoring the weather is critical for keeping track of changing conditions. Weather monitoring systems are critical in providing data for assessing environmental changes and climatic trends, aiding many fields such as agriculture, geology, and mining, and improving weather prediction models.

Components of a Weather Monitoring System
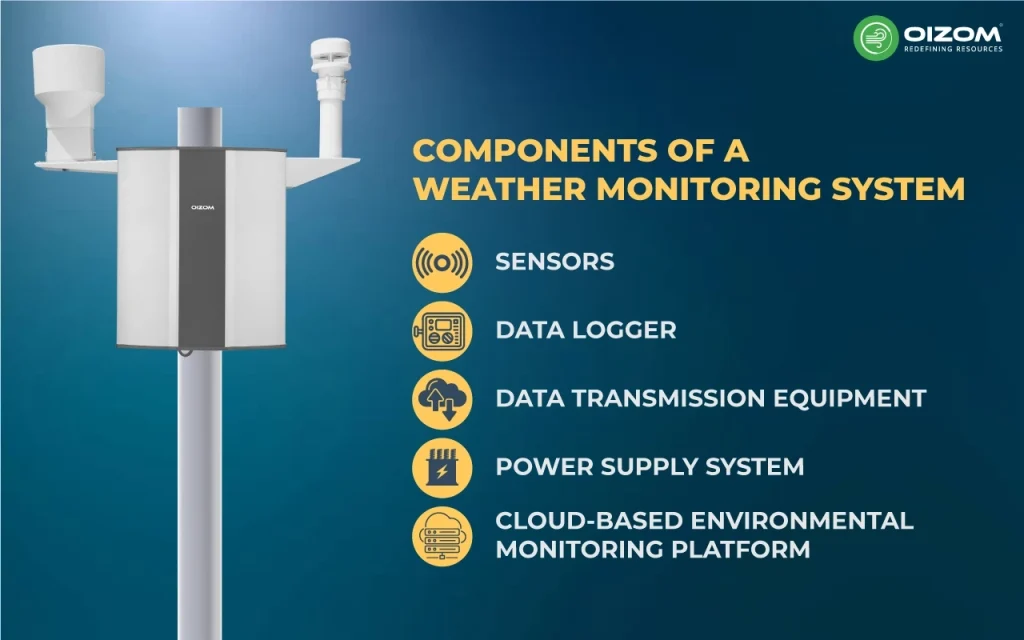
A weather station is a device used to monitor and record the parameters of the atmospheric environment. The outdoor weather monitoring system comprises weather sensors, a data logger, power supply systems, all-weather protection enclosures, data transmission equipment, and cloud-based environmental monitoring platforms. It consists of the following key components:
- Sensors
- Data logger
- data transmission equipment
- Power supply system
- Cloud-based environmental monitoring platform
Sensors
Weather sensors are those that keep an eye on what’s happening in the atmosphere. Imagine having a little device that can tell you the temperature, how humid it is, the air pressure, and even how much it’s rained. These sensors can also measure how fast the wind is blowing and from which direction, how much moisture is in the soil, and how much sunlight is hitting the ground.
The main job of these weather sensors is to gather all this data about the weather conditions around us. This information helps us understand the weather better and make accurate predictions. So, next time you check the weather forecast, remember there’s a whole bunch of these sensors out there working hard to keep you informed!
Weather stations include a number of sensors that measure and monitor various meteorological characteristics such as temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, wind speed, wind direction, precipitation, and so on. Each meteorological characteristic is usually assigned to a specific sensor, and the data acquired by the sensor indicates changes in the atmospheric environment.
- Temperature Sensor: A sensor that measures the temperature of the atmosphere.
- Humidity sensor: A device that measures humidity and relative humidity in the atmosphere.
- A barometer sensor measures atmospheric pressure.
- Wind speed sensor: a device that detects wind speed.
- Wind direction sensor: a device that detects the direction of the wind.
- Precipitation sensor: a device that measures rainfall.
- Solar radiation sensors monitor the sun’s ability to emit radiation. They are widely used in meteorology, environmental monitoring, and renewable energy applications.
Data Logger
- Modern monitors often include data logging and connectivity features. These features can benefit long-term trend analysis, remote monitoring, and integration with other safety systems.
- A weather station’s data logger is a device that receives and stores data collected by sensors. It typically has high precision and stability and can process and record data collected by sensors for later analysis and application.
Data Transmission Equipment
- To enable remote monitoring and data sharing, the weather station often requires data transmission equipment, such as wireless communication modules or network interfaces, to send collected data to a central database or other relevant systems.
Power Supply System
- The weather station requires a stable power supply system to guarantee that sensors and data recorders function properly. The power supply system may comprise solar panels, storage batteries, and other components to fulfill power demands in various environments. It can be utilized in the field for forest fire prevention, mountain flood monitoring, and other applications without a main power source.
Cloud-based environmental monitoring platform
- The weather monitoring cloud platform is a web login platform specially developed to provide users with the most convenient service. Imagine a station in the heat of the Sahara or the cold of the Arctic, continuously providing accurate data unhindered by the environment. That’s why Weathercom promises consistent, reliable, and undeterred meteorological monitoring.
- Oizom’s Advanced Air Monitoring Software for Professionals, Envizom, is an Environmental visualization and analytics platform for real-time air quality data acquisition. Our Environmental Data Interpretation Engine, powered by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms, provides highly accurate data and actionable insights, empowering users to make well-informed decisions.
How is Weather Data Collected and Analyzed?
Weather data is collected from a vast network of sources, processed by powerful computers, and analyzed by meteorologists to create forecasts.
Weather Monitoring Networks
Weather monitoring networks are systems of interconnected weather stations and technologies that collect, process, and share meteorological data. These networks are crucial for understanding and predicting weather patterns, ensuring public safety, and aiding various industries. Weather data is collected through a combination of ground-based stations, weather balloons, satellites, and radar systems.
Ground-based stations
These are spread across urban, rural, and remote areas. Each IoT weather monitoring system has sensors for temperature, humidity, wind speed, direction, and barometric pressure. These stations provide localized weather data and are often maintained by national meteorological agencies.
Mobile weather stations
- They are portable devices designed to measure various atmospheric conditions at different locations. Unlike fixed weather stations, these units can be easily transported and deployed in areas where weather data is needed.
- Mobile weather monitoring systems are portable devices ideal for temporary installations or circumstances requiring weather information, such as field studies, outdoor activities, or emergencies. These systems offer both versatility and ease of usage. Although they may not measure as many parameters as permanent systems, their mobility is critical for effective weather monitoring and data collection when on the move.
Satellite-based weather monitoring
- Today, there are approximately 200 meteorological satellites in orbit, with the vast majority falling into two categories. The first are polar-orbiting satellites, which orbit the Earth at low altitudes from pole to pole, tracking the entire planet’s rotation for 10 days to a month. On the other hand, Geostationary satellites orbit at high altitudes above the equator, moving at the same rate as the Earth’s rotation and continuously monitoring a certain area of the world. Both categories play critical roles in weather forecasting.
- Weather satellites are outfitted with various instruments, including temperature and humidity sensors, cameras for image capture, and tools for detecting other atmospheric phenomena such as wind speed and precipitation. In general, they are designed to be multi-functional, carrying a variety of sensors to offer thorough observations. Some, however, may concentrate on a certain variable.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, emerging technologies hold great promise for the future of weather forecasting. If you’re looking to understand what kind of weather sensors you need, Oizom Weathercom offers perfect solutions for monitoring weather. Today, weather forecasts are becoming more accurate and useful, Weather monitoring benefiting various sectors of the economy.
For instance, ports and harbors rely heavily on precise weather and air quality data to ensure operational safety and efficiency—topics we explore in detail in our Seaport Air Quality and Weather Monitoring Guide. The forecasting community collaborates closely with users to ensure forecast information meets their specific needs, enabling proper mitigation strategies before disasters strike. I hope this article explains how weather monitoring system work and their key components.
FAQs
Weather monitors are generally very accurate, especially modern ones equipped with advanced sensors. However, their accuracy can depend on factors like placement, maintenance, and the specific type of sensor used.
Most weather monitors take readings at regular intervals, typically every few seconds to every few minutes. However, this frequency can vary depending on the specific device and settings.
Yes, many weather monitors are designed for easy installation and come with detailed instructions. However, proper placement is crucial for accurate readings, so it is important to follow the guidelines carefully.
Weather monitors collect data on current conditions, which is used by meteorologists and forecasting models to predict weather. While they don't directly predict weather, they provide essential data that helps create accurate forecasts.






