10 Key Takeaways:
- Clean & Renewable: Solar power is a sustainable, zero-emission energy source that’s much kinder to the environment than fossil fuels.
- Solar Power Plant: It’s a facility that uses solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity for large-scale energy production.
- Types of Solar Plants: Solar power plants are classified into photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal types, each catering to different needs.
- Solar Thermal Process: These plants use sunlight to heat fluid, producing steam to generate electricity through a thermodynamic cycle.
- Photovoltaic (PV) Process: PV plants generate electricity by using sunlight to stimulate solar cells, producing direct current (DC) power.
- Key Components: The main parts include PV panels, inverters, energy storage devices, charge controllers, and system balancing components.
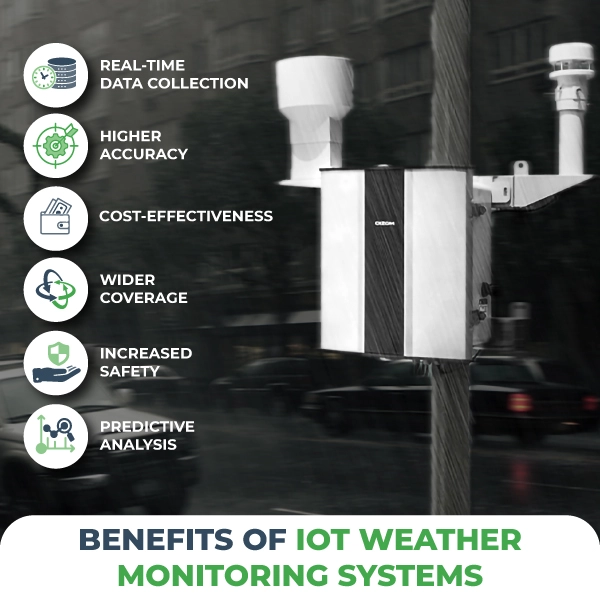
- Weather Monitoring: Oizom’s Weathercom helps solar plants optimize performance by providing real-time weather data.
- Benefits of Solar Power: Solar power plants have long lifespans, are low maintenance, noise-free, and can reduce energy transmission costs.
- Solar Farm vs. Solar Plant: Both terms refer to large-scale solar setups, but solar farms are often expansive ground-mounted systems in rural areas.
- Future Ready: Innovations like Oizom’s Weathercom enhance solar power efficiency, making it a dependable and sustainable solution to address rising global energy needs.
What is a solar power plant? Understanding Types, Components, and How It Works
Imagine a power source that’s not only clean but endlessly renewable, captured straight from the sun! That’s what a solar power plant offers: a way to generate electricity without harmful carbon emissions or environmental impact. With people everywhere waking up to the benefits, solar energy is swiftly becoming the alternative we can count on over traditional electricity sources.
As technology advances, solar power is becoming more accessible and affordable than ever before, making it possible for individuals, communities, and businesses alike to tap into this sustainable energy source. In this blog, we’ll dive into the different types of solar power plants, explore their key components, break down how they work, and highlight the many benefits of going solar.

Types of solar power plants
A solar power plant is a facility that converts solar energy, which consists of light, heat, and ultraviolet radiation, into electricity suitable for distribution to households and companies. Based on their operational system, solar plants are classified into two groups: thermal power plants and photovoltaic plants. Let’s know more about these types
Solar thermal power plant
A solar thermal plant is a facility that converts solar energy into electricity using a standard thermodynamic cycle. Unlike thermal power plants, which use fossil fuels, solar thermal power plants use a totally environmentally beneficial energy source, such as sunlight. The technology used to generate power varies slightly depending on the kind of solar thermal plant, but the operating mechanism is similar.
A solar thermal power plant concentrates solar energy to heat a fluid with thermally conductive qualities, raising its temperature until it becomes steam. The steam is then put into a turbine. The heat energy is transferred into mechanical energy, which is then transmitted to an alternator, where it is transformed into electricity. Once the thermodynamic cycle is completed, the steam is returned to a condenser, where it returns to a liquid state, and the process is repeated.
From an efficiency standpoint, it is critical to remember that a solar thermal plant’s performance is determined by the number of hours of sunlight and the meteorological conditions. As a result, modern power plants have a storage tank that allows the generated energy to be saved for later use.
Solar photovoltaic power plant
A solar photovoltaic plant operates using photons and light energy from the sun’s rays. These facilities employ different types of solar panels. Solar thermal plants employ collectors, but photovoltaic power plants use photovoltaic solar cells manufactured of silicon (monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels) or other photovoltaic materials (amorphous solar panels).
Because of the materials used, when the sun’s rays reach them directly, the electrons in the photovoltaic cells’ outer layers absorb the solar radiation and generate direct current power. To create a solar photovoltaic plant, these solar cells are joined in series and combined into a single module, generating photovoltaic panels.
In turn, the solar panels are joined in parallel to form strings that are connected to a current inverter. This inverter converts the direct current from the photovoltaic cells into alternating electricity. The electricity is then directed to a transformer, where its voltage and intensity are adjusted so that it can travel through the electrical grid lines to the consumption centers.
Key components of a solar power plant
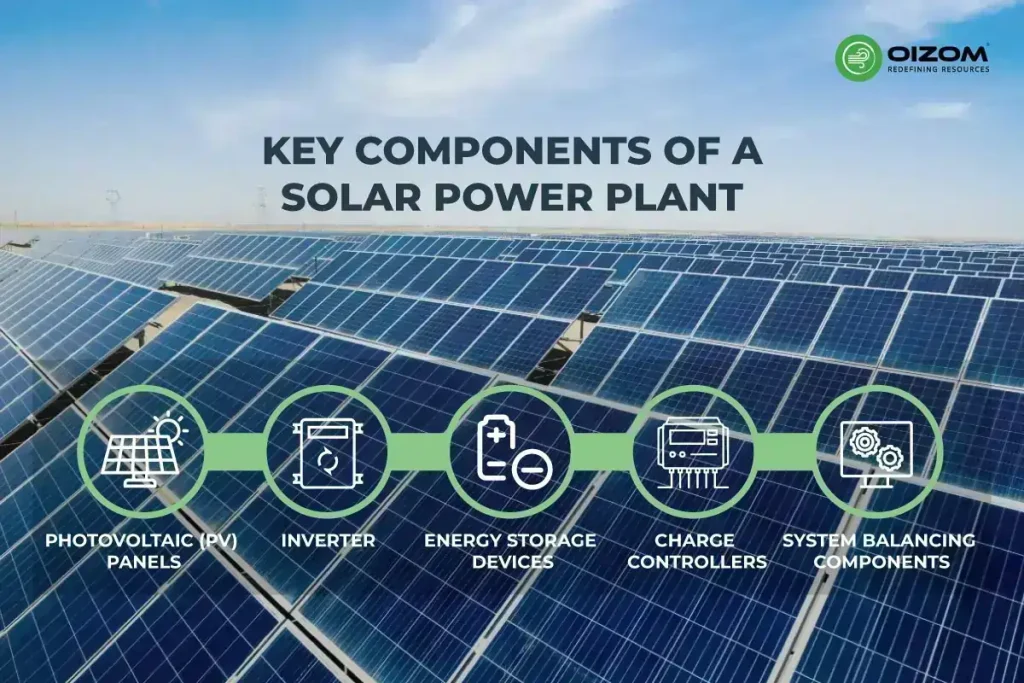
The main components of a solar photovoltaic system are mentioned below:
- Photovoltaic (PV) panels: A solar power plant’s most essential component is its PV panels, often known as photovoltaic panels. It is composed of tiny solar cells. This technology converts sun photon energy into electrical energy.
- Silicon is primarily employed as a semiconductor material in solar cells. Silicon solar cells are typically rated at 0.5 V and six amps. This is comparable to 3 W of power. The number of cells is joined in series or parallel to form a module. The number of modules constitutes a solar panel.
- A number of plates are mounted depending on the capacity of the power plant, and a collection of panels is also known as a photovoltaic (PV) array.
- Inverter: The solar panel produces direct current (DC). The majority of the load connected to the power system network is in the form of AC. As a result, we must convert DC output power to alternating current (AC). In solar power facilities, this is accomplished using an inverter.
- In a large-scale grid-tied power plant, the inverter is protected by special devices. A transformer is also attached to the inverter to ensure that the output voltage and frequency match the standard supply.
- Energy Storage Devices: Batteries are used to store the electrical energy produced by solar power plants. The storage components are the most significant components in a power plant because they fulfill demand and load fluctuations. This component is very useful when the sun is not available for a few days.
- The capacity of a battery refers to how much electrical power it can hold. Battery capacity is indicated in the Ampere-hours (AH) rating.
- For example, a 100 AH battery can provide a 1 amp current for 100 hours or a 100 amp current for one hour.
- There are two types of batteries used in the solar power plant;
Lead-Acid battery
Nickel-Cadmium battery
- Charge controllers: A charge controller controls the charging and discharging of the battery. The charge controller prevents battery overcharging. Overcharging a battery may result in corrosion and reduced plate development. In the worst-case scenario, it may cause harm to the battery’s electrolytes.
- Sometimes, the charge controller is referred to as a solar battery charger. Numerous technologies are utilized to create a charge controller. For example, the most used technology is the MPPT charge controller, often known as “Maximum Power Point Tracking.” This program optimizes the manufacture of PV cells.
- System balancing components: It is a set of components used to control, protect, and distribute power in the system. These devices ensure that the system works in proper condition and utilizes energy in the proper direction. It also ensures maximum output and security for other solar power plant components.
How does solar power work?
Solar energy is an abundant, limitless, and clean resource. Solar electricity generation is an excellent alternative to fossil fuel-generated electricity because it emits no pollution and poses no health risks. The energy we receive from the sun is amazing. Eighteen bright days on our planet contain as much energy as all fossil fuels combined. It is a wonderful possibility to transform that vast amount of energy into electricity via solar power systems. Photovoltaic (PV) systems typically comprise many solar panels that may convert energy into useful power.
Solar power generates electricity by converting sunlight energy. The sun generates two types of energy that we can use: electricity and heat. Both are created using solar panels, which range in size from home rooftops to ‘ solar farms’ that cover acres of rural terrain.
Oizom’s Weathercom system complements these solar power setups by delivering accurate, real-time weather insights. This data-driven monitoring helps optimize solar panel performance based on conditions like sunlight intensity, temperature, and humidity. With Weathercom, operators can adjust parameters to enhance the energy output and longevity of solar systems, making clean energy production even more reliable.

Benefits of solar power
Solar power has various advantages for individuals and organizations, as well as the environment:
- Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of energy that is unexhausted.
- After installation, the solar power plant generates electrical energy for nearly no cost.
- The lifespan of a solar plant is extremely long. Solar panels can last up to 25 years.
- This plant does not pollute the air.
- Solar cells do not contain any moving parts. As a result, solar plants do not require maintenance to function properly.
- It does not make any noise.
- For bulk generating, this plant can be placed on any land. As a result, no specific site selection criteria exist for thermal and hydropower projects.
- The solar plant can be mounted on a house or in a flat. As a result, it minimizes transmission costs by generating energy near the load center.
- In a grid-tied power plant, the electrical generated power can directly transfer to the grid, reducing the burden of conventional power plants.
Is a solar farm the same as a solar plant?
“Solar farm” and “solar power plant” are interchangeable. Both terms refer to the large-scale use of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels to create clean, renewable energy from the sun.
Solar farm
However, if we were to distinguish, a solar farm is typically defined as a huge array of solar panels erected on the ground in fields or deserts. They are frequently placed in rural or remote regions with abundant open ground. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), the country alone has over 2,500 utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) electricity-generating installations. While most solar farms are relatively small, collectively, they account for 2.5% of utility-scale electric generating capacity and 1.7% of annual electricity generation in the U.S. These facilities are designed to generate large amounts of electricity, frequently enough to power thousands of households.
Solar Plant
- It can refer to big installations, such as solar farms, and smaller, more localized facilities.
- A solar plant can be a commercial installation that powers a specific industry or a community-based enterprise that serves a specific area.
- Its size varies greatly, from a few panels on a city building’s rooftop to projects spanning several acres.
Conclusion
Finally, Now you know what a solar plant is and why you need one. You are also aware of the two popular types of solar plants. If you are looking for a versatile option, you can go with PV systems. Solar thermal systems can be great if you want a reliable source within a restricted space.
In conclusion, solar power is a remarkable, renewable solution to sustainably meet our growing energy needs, as it is much kinder to the environment than traditional energy sources. With advancements in technology and tools like Oizom’s Weathercom, solar power plants can maximize efficiency by monitoring essential weather data in real-time. This ensures optimal performance regardless of conditions, making solar energy even more reliable. Embracing solar power, supported by smart technology like Weathercom, is a key step towards a sustainable future for everyone.amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.