Real-Time Pollution Maps for Smart Cities

Real-Time Pollution Maps for Smart Cities
Written By : Ayyan Karmakar and Ankit Vyas Published On November, 2020
Download Whitepaper
Massive-scale urbanization, industrialization, and population growth along with an increase in vehicular traffic and energy use have made urban air quality a global concern. The distribution of air pollution concentration over a large urban area predominantly depends on local emission sources and atmospheric flow conditions. Also, smart cities are the centres of various activities having multiple and diverse pollutant sources emitting all kinds of air pollutants. As a result, the air quality of two points even within the same city-block may have a significantly different pollutant concentration. In order to maintain a healthy air environment, it is important to ensure the availability of fine-resolution air quality data and the ability to visualize on a pollution map. This paper focuses on benefits of such real-time pollution maps for smart cities.
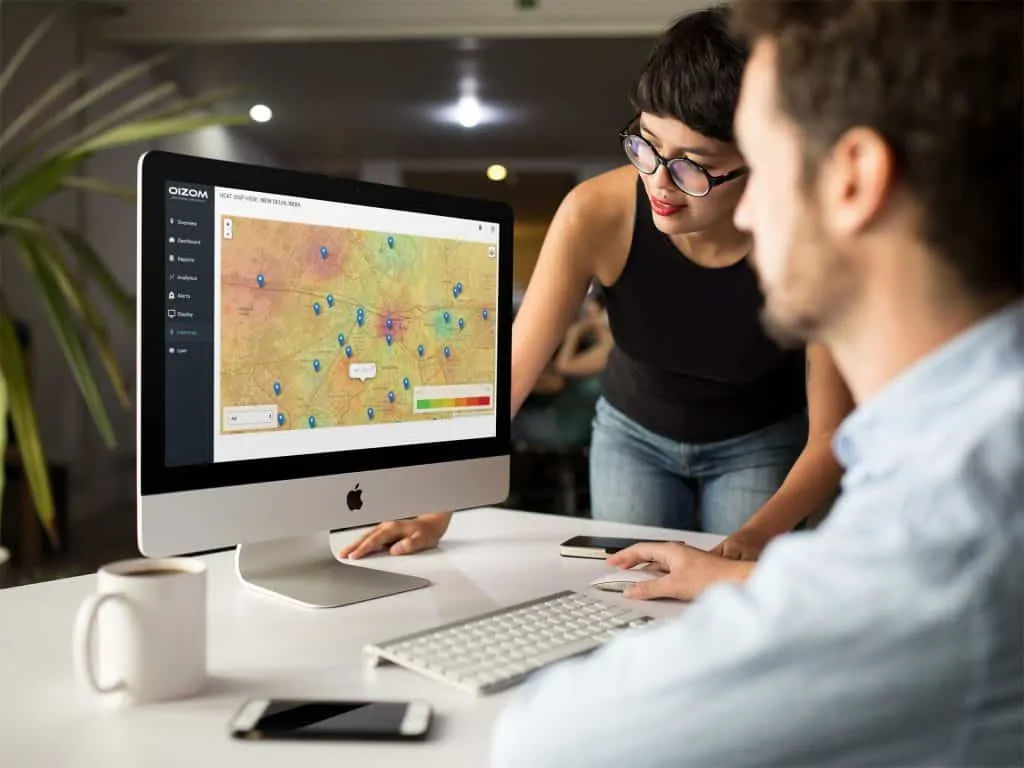
The traditional approach of monitoring air quality at a few selected locations cannot provide such an accurate representation of total urban air quality. This gap can be bridged by deploying multiple low-cost sensor-based systems, which are compact and can be installed virtually anywhere, from a roadside to a terrace or a pole. Such additional data points facilitate the development of real-time air pollution maps for the smart cities. Generation of pollution maps helps in understanding the spatial distribution of pollutants, which also enable hotspot identification. The paper explains various methods of data representation mapping air pollution concentration. It also develops an understanding of how real-time monitoring data can be integrated with secondary data such as meteorological data and traffic data to create dynamic air pollution maps. Such real-time air quality mapping provides great insights into the spatial distribution of air pollution, which enables the opportunity to make informed decisions and actions. Such a monitoring system and real-time pollution mapping capabilities serve the basis for designing and planning of smart cities. The paper also describes OIZOM’s offering of comprehensive and scalable solutions for environmental monitoring and analytics in the form of real-time maps for smart cities. The data generated are integration-friendly for various cross-platform applications, bringing together multiple stakeholders to provide data-driven solutions for smart cities.