Summary
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is only as reliable as the data supporting it, which is why Air Quality Monitoring (AQM) is crucial. Even though most LCA tools (excluding Europe) rely on outdated or European datasets and standards, real-time AQM data offers local, real-time emissions insights that traditional databases can’t match.
This blog explores how AQM can enhance the accuracy of LCA calculations by tracking pollutants like PM2.5, NOx, SOx, and VOCs, which control major LCA categories related to air, such as Global Warming Potential, Acidification, Smog Formation (POCP), and Particulate Matter Formation.
With a simple example of PET bottle manufacturing, we will understand how integrating AQM data into LCA will help companies to replace vague estimates with actual emissions, leading to better decision-making and context-specific environmental assessments.
To put it shortly, LCA needs data to predict the environmental impact, and AQM delivers it with accuracy, relevance, and impact.
Air Quality Monitoring and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
In regions other than Europe, companies working to conduct LCA face a significant challenge: the lack of accurate, localized emissions data. Where Europe benefits from well-established datasets, industries in other regions often have to rely on old information or general emission factors. This simply means LCA calculations may not reflect the exact on-ground reality, leading to inaccurate assessments.
This is where real-time air quality monitoring (AQM) comes in; it provides accurate, location-specific data on pollutants like PM2.5, NOx, and VOCs. AQM enables companies to provide necessary data, allowing for precise and actionable LCA calculations. With correct data, businesses can make informed decisions that are sustainable as well as aligned with actual environmental conditions.
The Importance of Accurate Data in LCA Calculations
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a systematic method used to assess the environmental impacts of a product, process, or service throughout its entire life cycle from cradle to grave. It empowers organizations by identifying possible environmental consequences during multiple stages, such as raw material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, usage, and disposal.
LCA provides critical insights to organizations aiming to enhance green initiatives and reduce their ecological footprint, giving them a sense of control over their environmental impact. To conduct an accurate LCA, it is important to focus on the impact categories that match the product being assessed. Although there are 14 different impact categories in LCA, they can be broadly grouped into three main areas: Air Quality, Water Quality, and Health & Ecosystem Impact.
Air Quality-Related Impact Categories

Several LCA categories are directly related to air quality, and real-time air quality data is important for accurately analyzing these impacts. These include:
- Global Warming Potential (GWP): This category focuses on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which affect climate change and contribute to rising air temperatures.
- Acidification Potential (AP): This assesses NOx and SOx emissions, which lead to acid rain, damaging both ecosystems and air quality.
- Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential (POCP): This category focuses on addressing the formation of ground-level ozone (smog), primarily driven by emissions like NOx and VOCs that harm air quality.
- Particulate Matter Formation: This category highlights the creation of fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), which impacts human health and local air quality.
Why LCA Needs AQM Data?
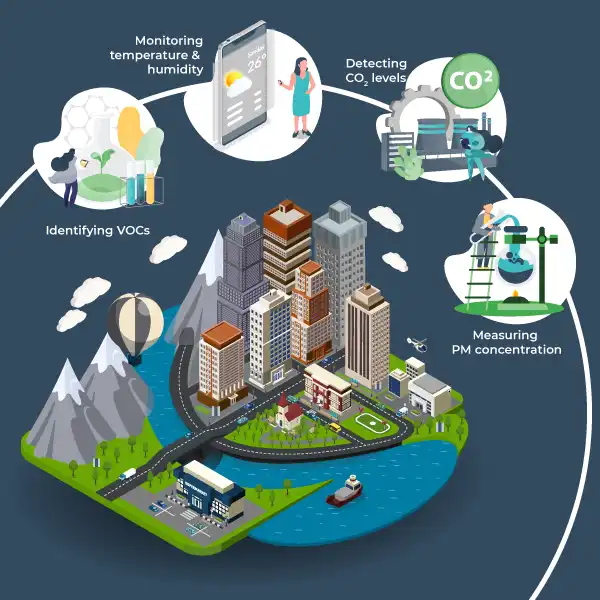
For a comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) that accurately evaluates a product’s environmental impact, real-time data on emissions of pollutants like NOx, PM, and VOCs at different stages of the product’s life is crucial. This is where Air Quality Monitoring (AQM) steps in, providing accurate, location-specific data on pollutants such as PM2.5, NOx, and VOCs, which are closely tied to product-related activities.
By integrating AQM data into LCA, businesses can accurately understand the air quality impacts of a product’s life cycle. For instance, if a product’s manufacturing emits NOx, contributing to smog, AQM data can be linked to LCA with insights into how these emissions will affect local air quality, ensuring better sustainability assessments.
In short, AQM data provides up-to-date data on pollutant levels, helping LCA accurately calculate the actual environmental impact, especially its effects on air quality.
How Real-Time Air Quality Data Improves LCA Accuracy?
Air Quality Monitoring (AQM) provides real-time data on pollutants, and while this data doesn’t directly provide CO2 equivalent (CO2e) values, it plays a crucial role in improving the accuracy of Life Cycle Assessments (LCA), which calculate the environmental impact of products. Understanding the importance of real-time air quality data in LCA accuracy enlightens and informs the audience, enhancing their knowledge in this field. Here’s how AQM data supports LCA:
Provides Real Emission Data for Accurate Impact Calculations:
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) often relies on emission factors to estimate the CO2e impact of a product. However, these factors can be refined and made more accurate with the help of real-world emission data provided by Air Quality Monitoring (AQM). AQM tracks real-time emissions from industries, vehicles, and other sources, providing a more accurate basis for CO2e calculations in LCA.
Localized Emissions Tracking:
Traditional LCA might rely on location-based averages, which can be inaccurate. Whereas, AQM provides localized data for specific areas, capturing variations in emissions from weather, industrial activities, and traffic patterns. This allows LCA to better estimate the true environmental impact of a product based on actual emissions from that region.
Real-Time Emission Variations:
Air quality data reveals how emissions change over time due to factors like seasonal changes or local events. For example, emissions might be higher during rush hours or industrial shutdowns.
Data Scarcity and the Role of Real-Time Air Quality Data
LCA data is often troublesome to collect and time-consuming, particularly in regions outside of Europe where there is a lack of accurate data. In regions where a country-specific LCA dataset is not readily available, companies often rely on outdated data or European standards for reference, which may not reflect local air quality conditions. The availability of real-time air quality data provides a sense of relief, offering accurate, location-specific insights and a clearer picture of real-time air quality than generalized data ever could.
Real-time air quality data helps solve this problem by providing accurate, location-specific insights. It takes into account local factors like traffic, industrial emissions, and weather patterns, offering a clearer picture of real-time air quality than generalized data ever could.
In short, AQM data helps LCA by providing real-time, localized emissions data, allowing for more accurate CO2e calculations and a better understanding of a product’s actual environmental impact.
Key Pollutants and Their Impact on LCA Calculations
A critical component of the LCA process is assessing the pollutants released during the different stages of the product. Pollutants such as PM2.5, NOx, SOx, and VOCs are the main contributors to environmental degradation and human health issues. Accurately monitoring and tracking these pollutants during the product life cycle is crucial for obtaining precise LCA results.
Monitoring these pollutants at various stages of a product’s life cycle provides detailed data, enabling businesses to assess the real-world environmental impact more accurately.
PM2.5 and Its Role in LCA
PM2.5 is a key pollutant in LCA because of its impact on human health. It relates to impact categories like Human Health and Particulate Matter Formation. Instead of relying on older estimates, using real-time PM2.5 data gives more accurate, local insights for LCA, leading to an accurate assessment of a product’s true environmental impact.
NOx Emissions and Their Contribution to Smog
NOx emissions impact key LCA categories like Photochemical Ozone Formation (smog) and Acidification. Real-time NOx data ensures these effects are accurately captured in LCA, avoiding underestimation of a product’s environmental and health burden.
SOx Emissions and Their Environmental Impact
SOx emissions affect Acidification Potential in LCA. Real-time SOx data helps capture the true environmental impact on ecosystems, enabling more accurate and location-specific sustainability assessments.
VOCs and Their Role in Air Quality
VOCs influence the Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential (POCP) in LCA. Real-time VOC monitoring can improve the estimation of smog-related impacts and support better environmental performance evaluation.
By accurately monitoring pollutants like PM2.5, NOx, SOx, and VOCs, businesses can ensure that their LCA calculations are based on real-world emissions data. This detailed and specific data not only improves the accuracy of LCA results but also helps businesses to make informed decisions about their sustainability efforts and environmental impact.
Real-World Applications: How Accurate Air Quality Data Enhances LCA?
Integrating real-time air quality data into Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) can significantly improve the accuracy of environmental impact assessments. A great example of this is in the manufacturing of PET bottles. The production of PET bottles involves multiple processes that emit PM2.5, NOx, SOx, and VOCs. By integrating real-time air quality monitoring (AQM), businesses can get actual emissions data, leading to precise LCA calculations and better knowledge of a product’s environmental impact.
Practical Example: PET Bottle Manufacturing

The manufacturing of PET bottles is a multi-step process including polymerization, extrusion, blow molding, and packaging. The manufacturing stage especially releases pollutants like PM2.5, NOx, and VOCs. LCA calculations for PET bottles rely on average emission estimates from similar processes. However, by integrating real-time air quality data from AQM systems into the LCA process, we can track actual emissions from their targeted production lines.
For instance, a PET bottle manufacturer can install air quality sensors at various points in the production process to monitor NOx and PM2.5 emissions. This data allows them to assess the real-time contribution of their operations to local air quality and refine their LCA to more accurately calculate the environmental impact of producing each bottle.
How Oizom Can Help?
Oizom provides real-time air quality monitoring solutions. Devices like Dustroid (PM), Odosense (VOCs/odour), Polludrone (fenceline air quality), and AQBot are widely used across industries. These sensor-based systems offer accurate, localized data continuously. They’re adaptable for ambient air, with options like Weathercom for tracking temperature and humidity.
The data is visualized and managed through Envizom, which is Oizom’s web-based platform that offers dashboards, smart alerts, reports, and API integration. This makes it easy to feed real-world emissions into LCA tools, ESG audits, and green certifications, supporting credible and compliant sustainability reporting.
Conclusion
As the interest in predictive LCA grows, real-time data is becoming the pillar of more accurate, reliable sustainability reporting. By integrating AQM solutions into LCA, businesses can shift from outdated estimates to using precise, real-time emissions data. This shift not only helps companies make better decisions today but also helps them tackle future environmental challenges with confidence.
Including accurate air quality data into sustainability strategies allows for enhanced reporting, planning more effectively in the future, and staying ahead of compliance standards. Here we conclude that the future of LCA is data-driven, and adopting this shift will empower organizations to build a more sustainable tomorrow.