The steel manufacturing industry is one of the largest in the world. Steel is primarily derived from iron ore, with 98% of mined iron ore manufacturing steel. This is a general overview of how steel is produced. In addition to being two of the most energy and carbon-intensive businesses, the steel and cement industries are also two of the top air polluters in the world.
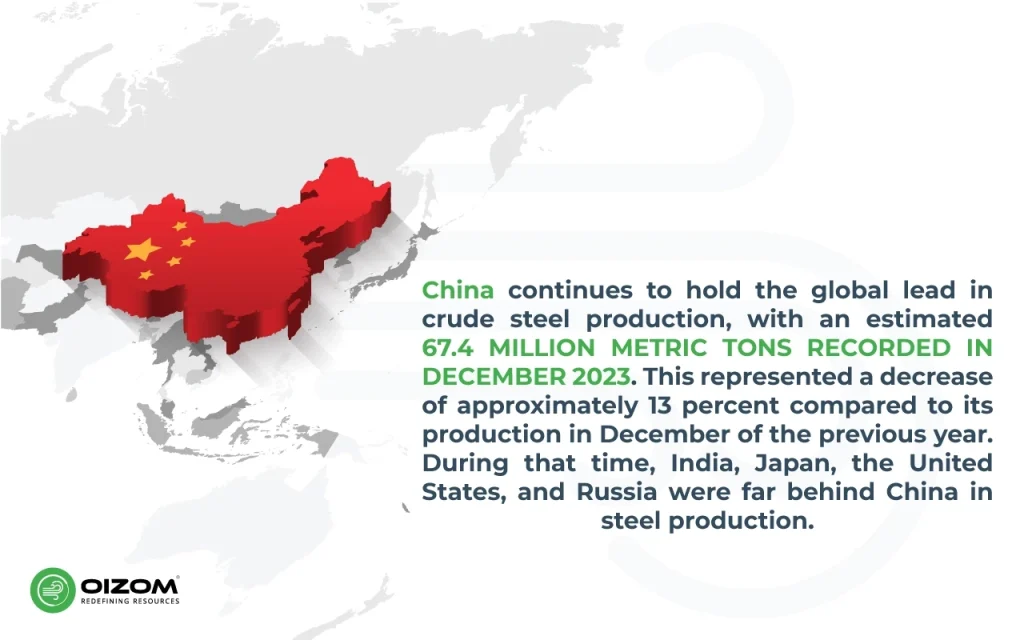
Steel is an important commodity because it supports many other industries, including buildings, automobiles, machinery, electrical equipment, and a wide range of products, from cookware to furniture. The world’s steel demand is projected to increase from 1,880 Mt (million tonnes) in 2020 to 2,500 Mt in 2050. By 2050, the steel demand is expected to increase fivefold. The steel manufacturing is energy-intensive and releases various pollutants, including carbon dioxide and particulate matter (PM). In this blog, we will gain a better understanding of controlling air pollution in the steel industries through various green practices to follow the steel industry. Did you know that India is the second-largest steel producer in the world after China.
How to Control Pollution in the Steel Industry: Effective Measures and Air Pollution Control Systems
The demand for steel is anticipated to increase more and more, as is the pollution caused by steel manufacturing. The first stage is to mine iron ore, which can be characterized simply as the first step in producing steel from iron ore. This is a very polluting process that involves blasting with coal, among other things. It emits various pollutants, including sulfur oxides, particulate matter, and fugitive dust. This is why air pollution control systems are the need of the hour in our country.

1. Understanding the Pollution Challenges in the Steel Industry
- Environmental Impact of the Steel Industry: Steel manufacturing is energy-intensive and releases various pollutants, including carbon dioxide and particulate matter (PM).
- Sources of pollution in steel manufacturing: Coke, a type of coal, is an important component in the making of steel, yet it is very detrimental to the environment. Coke ovens emit very toxic and carcinogenic naphthalene into the air. The wastewater from the coking process is also exceedingly hazardous, containing cyanide, sulfides, ammonium, and ammonia, among other organic chemicals known to cause cancer.
2. Implementing Technological Advancements for Pollution Control
- Introduction to Advanced Pollution Control Technologies: Pulse Jet Bag Filters, Cyclones, Electrostatic Precipitators, Mist Collectors, and Wet Scrubbers are some of the most modern pollution control equipment available today.
- Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP) for Particulate Matter Control: Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), like air filters and cyclones, are air pollution control devices that gather and remove particulate matter (dust) from industrial emissions and exhaust. ESPs have 99.9% efficiency, making them a great choice.
- Scrubbers For Gas Cleaning: Industrial air scrubbers use physical processes to remove particles and gases from industrial pollutants such as smokestack exhaust before releasing them into the atmosphere via water spray.
- Scrubbers For Gas Cleaning: Industrial air scrubbers use physical processes to remove particles and gases from industrial pollutants such as smokestack exhaust before releasing them into the atmosphere via water spray.
- Baghouses For Dust Collection: Bag filter dust collector systems are a type of dry dust filtration equipment used in cement plants, lime factories, coal powder preparation units, and other applications. It includes benefits such as increased air volume, improved dust cleaning capabilities, high efficiency, and ease of operation and maintenance.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) for NOx Control: The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) process eliminates nitrogen oxides (NOx) from flue gas produced by power plant boilers and other combustion sources.
- Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS): A continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS) is necessary for determining a gas or particulate matter concentration or emission rate using pollutant analyzer measurements. Oizom devices such as Polludrone can accurately monitor various gas concentrations or PM and provide real-time monitoring data using our Air Quality Monitoring Software – Envizom.
3. Utilizing Efficient Energy Sources
- Renewable Energy Integration: Integrating renewable energy requires reinventing operations and planning for a dependable, cost-effective, and efficient electrical system powered by cleaner new energy producers.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Energy recovery systems collect exhaust heat from energy-consuming processes or exhaust stacks and use the excess energy to warm process, plant, and combustion air.
- Energy Efficiency Measurements: Energy efficiency, together with the closely linked criteria of electrification, behavioral change, digitization, and material efficiency, is the most important measure for reducing energy demand in the Net Zero Emissions framework.
4. Promoting Waste Management and Recycling
- Steel Scrap Recycling: Scrappers collect steel scrap individually at designated drop-off places or buy-back facilities. Following that, it is sorted and transported to mills or foundries. A furnace is then used to melt down the remaining steel scrap.
- Slag and fly ash use: FlyAsh, produced in coal-fired thermal power stations, is utilized as a raw material by firms that manufacture cement and building supplies. It is also used to construct roadways and flyover embankments, which helps prevent soil degradation and preserve profitable agricultural land.
- Water Conservation and Recycling: Water recycling is the process of reclaiming water from diverse sources, treating it, and reusing it for useful purposes such as agriculture, irrigation, and other applications.
5. Encouraging Government Regulations and Compliance
- Environmental Laws and Policies: Any governing body must incorporate environmental legislation as a key component. It comprises a system of regulations and legislation governing environmental issues such as water and air quality.
- Compliance Monitoring and Reporting: To discover compliance risk issues in their normal operations and functions, organizations must adhere to rules and procedures that are monitored as part of the compliance monitoring process
- Collaboration with Regulatory Authorities: A regulatory authority is a government-established independent enforcing agency that supervises and enforces occupational health and safety regulations. The regulatory authority’s mission is to establish and strengthen safety standards while ensuring that they are regularly implemented.
6. Collaborating with Air Pollution Control System Manufacturers: Introducing Techflow
- Our Commitment to Innovation: Our organization is driven by technology and innovation in operations and product design. Various models have been developed as high-efficiency models for pulse jet bag filters & high-performance designs for centrifugal fans.
- Customized Solutions and Cutting-Edge Technologies for the Steel Industry: Using advanced sensors, cutting-edge technologies, and data analytics, Oizom systems can accurately measure various pollutants emitted from steel plants’ in the air. This real-time monitoring allows for timely and effective responses to toxic gases, PM, and other relevant pollutants. For instance, in areas where industrial activities are causing elevated AQI levels, Oizom’s data can prompt immediate mitigation measures, such as enabling long-term planning and policy-making to control industrial emissions more effectively. By providing actionable insights, Oizom empowers communities and authorities to make informed decisions, leading to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Notable Green Practices to Follow in the Steel Industry
The steel industry has been instrumental in pursuing sustainable strategies such as those listed below:
Sustainable Light Steel Frame Construction
This kind of steel construction uses pre-engineered components that are simple to assemble and disassemble. Steel frame construction requires less extensive foundations and takes less time. They significantly minimize pollution from building sites.
Packaging with Steel
- Steel contributes significantly to the circular economy since it can be continually recycled and produced without losing quality. Companies like Unilever have begun to use the benefits of steel by packaging consumer items like shampoos in steel bottles and jars.
- Aluminum and steel are two of the most recycled materials in the world. Instead of extracting new metal from the earth, most companies that use metal packaging use materials that are at least partially recycled. It is estimated that 80% of worldwide metal is still in use today.
- Many customers seek solutions to lower their carbon footprint and live more environmentally friendly lives. Metal is widely acknowledged to be easy to recycle and to pose fewer threats to people and the environment than plastic, so utilizing it to package your items can help you connect with environmentally conscious customers.
Using Slag to Sustain Marine Environment
Since 2007, steel companies such as POSCO in Japan have used slag containers (a byproduct of steel) to combat the desertification of marine algal forests along the South Korean coast. Slag is a thick, rocklike substance. Algae are planted in slag containers, and their density and weight protect the algae forests from typhoons and tsunamis.
However, the primary step towards sustainability is acknowledging and addressing the pollution emitted in steel production. This safeguards employees’ health and ensures pollution does not impact surrounding areas. This is irreplaceable and takes precedence over most other practices.
What is the current status of pollution in the steel industry?
The steel sector is the third-largest contributor to air pollution and one of the leading drivers of industrial pollution in India, with the highest carbon dioxide emissions. Steel, in particular, requires coal for energy; therefore, burning coal generates significant emissions. Steel plants emit various air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), carbon dioxide, sulfur, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide.
Challenges in Pollution Control - Fugitive Emissions
‘Fugitive’ emissions are a key concern for the steel industry. Fugitive dust definitions apply to’ fugitive’ pollutants or escape from a source without being accounted for. Regular emissions from established sources are accounted for, making them easier to monitor and control. In contrast, fugitive emissions are difficult to trace because their source is unclear. As a result, they unknowingly contribute to ambient air pollution. The problem of fugitive emissions arises at every level of the steel manufacturing process and presents a significant obstacle.
“Join us as we delve into the Oizom case study for monitoring air quality in the steel manufacturing industry, showcasing the power of smart technology in environmental preservation.”
Conclusion
So, how to control air pollution in the steel industry? The key solutions include adopting cleaner manufacturing technologies like electric arc furnaces, using low-emission raw materials, implementing advanced air pollution control equipment such as bag filters and scrubbers, and improving energy efficiency across operations.
Additionally, monitoring emissions in real time with air quality monitoring systems like Oizom’s devices and Envizom software helps steel plants stay within permissible limits and take immediate corrective action.
Beyond technology, the steel industry must also focus on better waste management, promoting recycling, adopting circular economy practices, and strictly following environmental regulations. Raising awareness about environmental responsibility among employees and local communities plays a crucial role too. Together, these steps not only reduce air pollution but also move the steel industry toward a more sustainable and responsible future.