10 key takeaway points:
- Advanced Technology Integration: Digital weather stations combine sensor technology, data processing, and communication systems for accurate weather monitoring.
- Real-Time Monitoring: They provide real-time weather updates, ensuring timely and precise information.
- Key Components: The system includes sensors, a data logger, data transmission equipment, and a reliable power supply unit, often solar-powered.
- Versatile Sensors: Measures temperature, humidity, wind speed, direction, air pressure, rainfall, sunshine, and noise levels for comprehensive data collection.
- Seamless Data Transmission: Outdoor sensors send data wirelessly or via cables to indoor display units for easy access.
- Wide Applications: Used in meteorology, agriculture, urban monitoring, transportation, disaster prevention, education, and more.
- Business Benefits: Provides real-time data, greater accuracy, cost-efficiency, broader coverage, enhanced safety, and predictive insights.
- Disaster Mitigation: Helps predict and manage natural disasters, aiding industries like tourism affected by extreme weather.
- Data Sharing and Alerts: High-tech systems offer alerts for severe weather and share data with networks for broader analysis.
- Future Ready: Digital weather stations continue to evolve, becoming smarter, more efficient, and essential for connecting people with the environment.
How does a digital weather station work? A Quick Guide
Have you ever wondered how modern weather stations provide accurate, real-time weather updates? Over the years, weather stations have evolved dramatically from simple analog devices with mechanical gauges to advanced digital systems. This transformation, driven by technological progress, has revolutionized how we monitor and predict weather. Digital weather stations now deliver precise data on temperature, humidity, wind, and more, all at your fingertips.
Whether you’re a weather enthusiast or a professional, these systems have become indispensable for understanding atmospheric conditions. We all keep an eye on the weather to plan activities, pick outfits, or decide whether it’s a day for the beach or an umbrella. From tracking unexpected rain showers to planning perfect picnics, weather insights have become an integral part of our daily lives. These weather systems have become indispensable tools. Let’s uncover how these modern devices work and why they’re essential in today’s fast-paced world.
Overview of digital weather station work
A Digital Weather Station (DWS) is a system that uses sensors and electronic devices to measure and record weather conditions like temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, air pressure, and rainfall. It gathers weather data from the environment using advanced sensor technology and displays the information on electronic screens.
The system has two main parts: an outdoor sensor unit and an indoor display unit. The outdoor unit is placed in an open area to get accurate readings of weather conditions like temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind, and rainfall. These sensors send real-time data to the indoor display unit through wired or wireless connections, such as Wi-Fi or RF signals, for easy viewing and analysis.
Components of a Digital Weather Station
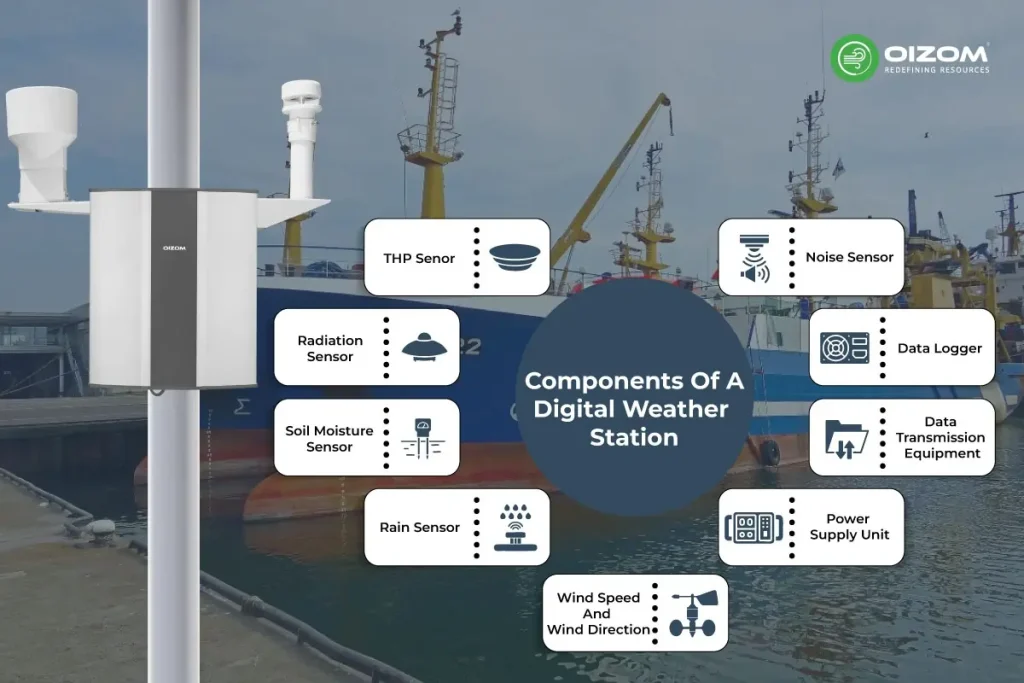
The digital weather station consists of the following main components: Sensors, a data logger, data transmission equipment, and a power supply unit.
Sensors: Weather stations are equipped with various sensors to measure and monitor different weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed, wind direction, rainfall, and sunshine. Each type of weather condition is measured by a specific sensor, which helps track changes in the atmosphere. Here’s a breakdown of the key sensors:
- Temperature Sensor: Measures the air temperature.
- Humidity Sensor: Measures the moisture and relative humidity in the air.
- Barometric Sensor: Measures atmospheric pressure.
- Wind Speed Sensor: Measures how fast the wind is blowing.
- Wind Direction Sensor: Identifies the direction the wind is coming from.
- Precipitation Sensor: Tracks the amount of rainfall.
- Sunshine Sensor: Measures the intensity of sunlight and UV radiation.
- Noise Sensor: Measures the level of ambient noise in the environment.
Data Logger: The equipment that receives and stores the data gathered by sensors is called a weather station data logger. It can analyze and record the data gathered by the sensors for later analysis and use, and it typically has great precision and stability.
Data Transmission Equipment: The weather station typically has to have data transmission equipment, including network interfaces or wireless communication modules, in order to send the gathered data to the central database or other relevant systems, enabling remote monitoring and data exchange.
Power Supply Unit: For the sensors and data recorders to function normally, the weather station requires a dependable power supply system. To fulfill the power requirement under various climatic conditions, the power supply system may consist of solar panels, wind turbines, storage batteries, etc. Were you aware of this? Whether your devices are in an off-grid location or a remote area, you don’t need to worry. Oizom Weathercom can run fully on solar power, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Benefits of Using Digital Weather Stations
The goal of weather monitoring is to use advanced technology to provide accurate, real-time data. In today’s world, where unpredictable weather can greatly affect various industries, having a dependable weather monitoring system isn’t just helpful. it’s essential. These smart systems use multiple sensors to gather and analyze weather data, delivering timely and precise information to improve daily life and business activities.
Did you know this? The tourism industry is especially vulnerable to extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes. The effects of these storms can last for months or even years. For example, tourism makes up 6.5% of Puerto Rico’s economy, with a record 8.1 million visitors in 2016. However, after Hurricane Maria hit in October 2017, the island was severely affected. By 2019, tourist numbers were still 36% lower than in 2016.
With advancements like digital weather monitoring systems, they are now faster, more consistent, and more highly accurate. But what does this mean for businesses? Here are the key benefits:
- Real-time data collection
- Greater accuracy
- Cost-efficiency
- Broader coverage
- Enhanced safety
- Predictive insights for better planning
Common Applications of Digital Weather Stations
Digital weather stations are widely used across various fields due to their accuracy, automation, and real-time capabilities. Here are some key applications:
- Meteorology: Provides accurate data for weather forecasts and climate studies.
- Urban Monitoring: Tracks real-time weather changes to understand city environments.
- Agriculture: Helps farmers plan activities and boost efficiency with weather insights.
- Transportation: Offers weather updates to enhance traffic management and safety.
- Disaster Prevention: Aids in predicting and managing natural disasters effectively.
- Commercial Use: Supports safety and operations in airports, ports, and outdoor events. Discover how Oizom Weathercom provides exceptional weather monitoring solutions to Portlinks India by diving deep into our case study.
- Home & Office: Monitors indoor and outdoor conditions for better comfort and energy use.
- Education & Research: Used in schools and labs for meteorology education and studies.
- Aviation & Navigation: Ensures safe flights and marine operations with real-time data.
How Does a Digital Weather Station Work?
Have you ever wondered how a digital weather station delivers accurate, real-time weather updates? It’s simple yet fascinating! A digital weather station is an intelligent weather monitoring device that combines sensor technology, signal processing, computer systems, and communication tools. It uses advanced sensors to measure weather conditions like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and rainfall.
These outdoor sensors gather data and wirelessly send it to an indoor display unit. With cutting-edge technology, the system processes this information instantly, giving you precise weather insights right at your fingertips. Whether it’s for planning your day, managing a farm, or ensuring safe travel, digital weather stations make weather monitoring smarter and more reliable. Let’s dive deeper into how these amazing devices work.
Steps in the Working of a Digital Weather Station
Are you curious about how a digital weather station works? Let’s break it down step by step:
- Data Collection: Advanced sensors placed outdoors measure various weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, air pressure, and rainfall. Some systems even track sunlight and noise levels.
- Data Transmission: The gathered data is transmitted to the indoor display unit, either wirelessly via Wi-Fi or RF signals or through wired connections, ensuring seamless communication.
- Data Processing: Using signal processing and computer technology, the station processes the raw data to make it meaningful and accurate.
- Data Display: The processed information is displayed on a user-friendly indoor unit, often featuring digital screens or app integration for real-time monitoring.
- Data Storage: Many digital weather stations have built-in storage or cloud integration to log data over time for analysis and trends.
- Alerts & Insights: Some systems offer alerts for extreme weather conditions or provide predictive insights to help you make informed decisions.
- Data Sharing: High-tech models can share weather data with online platforms, apps, or networks, contributing to community weather updates or professional analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital weather stations have transformed how we monitor and predict weather by combining advanced technologies like sensors, data processing, and communication systems. They provide real-time, accurate data that supports industries like agriculture, transportation, and disaster management, making them essential tools in today’s world. As technology advances, these stations are becoming smarter and more efficient, helping us connect with and better understand the natural environment. Their evolution from simple analog devices to modern digital systems highlights their importance in shaping the future of weather forecasting.