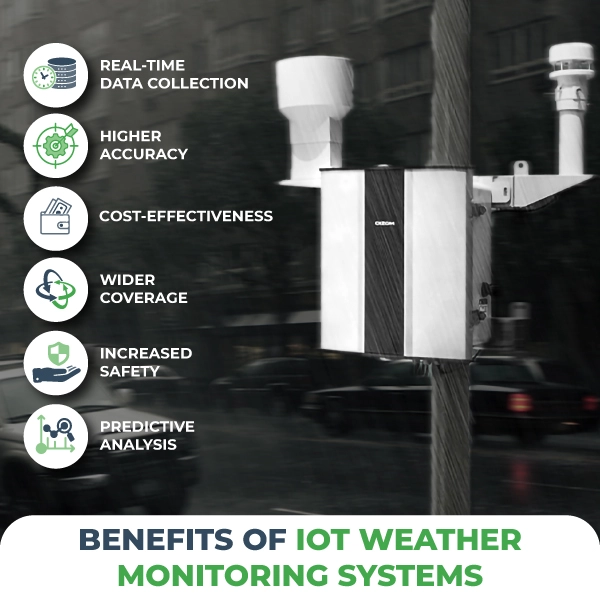
key takeaway points
- Sources of air pollution: transportation, industry, energy production, agriculture.
- Major pollutants: carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, greenhouse gases.
- Ways individuals can help: use public transportation, practice energy efficiency, adopt responsible consumption habits.
- Importance of air quality monitoring with advanced technology like Oizom devices.
- Collective responsibility to prioritize health and create cleaner, livable cities.
What are ways to reduce air pollution? Know more: Practical Tips to Lower Air Pollution
Have you been getting sick? Or are you complaining of a headache, an unpleasant mood, and a sore throat? Air pollution is invisible yet harmful to human health. With the pollution levels in the sky, no one appreciates the summer heat anymore.
Air pollution is now at an all-time high in the country, making it difficult for people to breathe clean air. Air pollution is a growing concern worldwide as people become more aware of environmental issues. You may question why we’re talking about air pollution, but in the twenty-first century, knowing whether the air you breathe is clean or less polluted is essential. Understanding the Causes of Outdoor Air Pollution is crucial in addressing this issue effectively.
Let me share stats with you regarding air pollution:
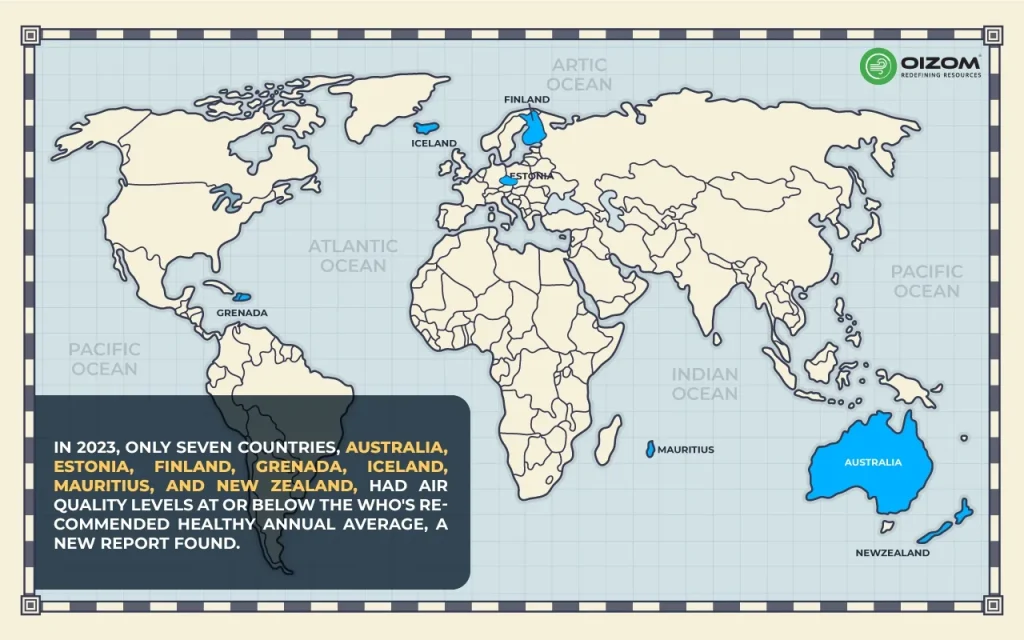
Moreover, walking outside or jogging has become daunting, especially with poor air quality. Hence, it is important to keep an eye on the air quality. In this article, I will discuss several methods to reduce air pollution and its various sources.
Major Sources of Air Pollution

Air pollution occurs when excess amounts of pollutants enter the atmosphere. This article presents an overview of the hazardous pollutants produced by anthropogenic sources.
Transportation Sector
- Pollutants emitted by petrol and diesel engines in cars, ships, trains, and other vehicles include carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Friction from tires and brake wear also produces primary (direct) particulate matter emissions. In addition, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by cars undergo photochemical reactions to form ozone (O3).
- In the UK, there is one car for every two people. Road transport contributes 80% of roadside nitrogen dioxide pollution, exceeding legal limits. Increased traffic affects air quality, causes noise pollution, reduces physical activity, limits access, and increases road collisions.
Were you aware of this? The UK’s capital has been ranked as the city most affected by aviation air pollution in a new global study tracking the world’s largest airports. The air pollution from planes taking off and landing at six airports in London equates to the equivalent of 3.23 million cars worth of harmful nitrogen oxides and particulate matter emissions every year.
Industrial Activities
The combustion of fossil fuels such as coal and oil in industrial processes in power plants, refineries, and factories emits a wide range of pollutants, most of which are identical to those generated by transportation and mobility. In addition, chemical processes and volatile industry wastes emit VOCs.
In the United States, industrial sources such as manufacturing, food processing, mining, and building account for over a quarter (23%) of total greenhouse gas emissions. These direct emissions originate from many activities, including on-site combustion of fossil fuels for heat and power, non-energy usage, and chemical processes used to make iron, steel, and cement.
Energy Production
Using fossil fuels to generate power and heat contributes significantly to global emissions. Most electricity is still generated by burning coal, oil, or gas, which emits carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide.
These two potent greenhouse gases blanket the Earth and trap the sun’s heat. Wind, solar, and other renewable sources generate little more than a quarter of global electricity and, unlike fossil fuels, emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants into the atmosphere.
Agriculture Practices
Fertilizer manufacturing, agricultural machinery, and livestock waste management in agriculture all contribute to various nitrogen molecules (NO, NO2, N2), including ammonia (NH3). In addition, animals digestive processes emit methane (CH4).
Agricultural practices, including tilling, harvesting, and livestock management, release dust particles into the air. These activities, especially in large-scale tree plantation, can significantly contribute to atmospheric dust levels.
Individual Actions for Cleaner Air

Air pollution is a growing concern, but individual actions can make a significant difference in improving air quality. One of the most effective natural solutions is planting trees. But how do trees reduce air pollution? They absorb harmful pollutants, filter particulate matter, and release clean oxygen, making them essential for a healthier environment.
Beyond planting trees, In this article, I will share several approaches for individuals to reduce air pollution and encourage sustainable living in urban areas.
Transportation Choices
Use public transportation to help reduce air pollution. Facts and data don’t lie: transportation accounts for 30% of total carbon dioxide emissions. We can use public transportation instead of private cars or vehicles.
Assuming a bus can transport 40 passengers at once, these 40 passengers can reduce the emissions of 40 private automobiles by taking one public vehicle instead. Many public vehicles rely on compressed natural gas (CNG).
CNG contains a substantial quantity of methane (CH₄). CH₄ burns cleaner than other fuels, resulting in lower ash emissions. As a result, it lowers the concentration of fine particles in the air.
The introduction of new technology, such as E-Busses, aids in reducing emissions and, consequently, air pollution. Traffic congestion emits significant levels of soot and carbon monoxide, contributing to poor air quality. Using public transit decreases pollution and traffic congestion on the road.
Energy Efficiency at Home
Avoid wasting electric energy and money. When you or your family members are not present, or the lights are not in use, turn them off with extreme caution and responsibility. Electricity plants burn fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to air pollution. To save energy, turn off lights whenever you leave a room.
Light bulbs are the least efficient sort of lighting; therefore, they should be turned off when not in use. Only around 10% of the power is converted for lighting, while the other 90% is transferred to heat. Turning off the lights will help keep the room cooler, which is helpful in the summer.
Encouraging the use of energy-efficient appliances, encouraging renewable energy sources, and implementing energy-efficient building rules can all help to reduce air pollution in cities. Adopting sustainable energy methods can enhance air quality while lowering greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Responsible Consumption Habits
Responsible consumption seeks to include social, environmental, and ethical considerations in purchase decisions. Consumers who support this model are well-informed individuals who want to reduce their environmental footprint while positively contributing to society.
When it comes to combating excessive consumption, sustainable purchasing follows the following principles:
- Reduction: The goal is to restrict consumption while evaluating the need for specific purchases.
- Energy efficiency: Customers also want efficient products that are low-consumption and can be reused or recycled.
- Sustainability: Finally, customers ensure that the components have no detrimental environmental impact once the item has reached its useful life
Conclusion
Finally, It is clear that air pollution is a significant concern for cities. As stated in this article, pollutants arise from various sources, and it is not always evident where they originate. This makes controlling air pollution challenging. Hence, high-resolution data from the urban environment is needed in order to identify the sources.
By monitoring the air quality with Oizom devices, which work on e-breathing technology and provide real-time data on cloud software. Moreover, these devices are compact, easy to install, and robust enough to provide accurate data even in harsh weather conditions.
Understanding Do Electric Vehicles Reduce Air Pollution is crucial in this effort, as EVs play a key role in minimizing harmful emissions and improving urban air quality. It is our joint responsibility to prioritize urban populations’ health and well-being by combating air pollution and building cleaner, more livable cities for future generations.
FAQs
Use Clean Energy: Switch to renewable sources like wind and solar.
Improve Public Transport: Reduce vehicle emissions by enhancing public transit.
Enforce Emission Standards: Implement stricter regulations for industries and vehicles.
Increase Green Spaces: Plant more trees in urban areas.
Promote Recycling: Reduce waste by encouraging recycling.
Support Innovation: Invest in new pollution control technologies.
Protect Health: Prevent diseases caused by polluted air.
Save the Environment: Protect ecosystems and wildlife.
Fight Climate Change: Reduce greenhouse gases to mitigate climate change.