Summary
The pulp and paper industry is fundamental to daily life, which produces products used globally across multiple sectors. However, it is also an influential contributor to air pollution, releasing various pollutants and greenhouse gases during key manufacturing steps such as wood preparation, pulping, bleaching, drying, and chemical recovery. Odorous gases from chemical pulping and bleaching also affect local air quality.
To mitigate these challenges, advancements in cleaner technologies, fuel switching, and pollution control equipment are helping reduce the process’s negative impacts. Similar to these solutions real-time air quality data provides crucial data for early detection, regulatory compliance, and process optimization.
This blog gives a brief understanding of the main pollution sources in the pulp and paper sector, effective reduction strategies, and sustainable alternatives. With the integration of awareness and technology, the industry can balance sustainability, encouraging the use of eco-friendly alternatives of paper and supporting greener manufacturing practices.
Air Pollution in the Pulp & Paper Industry
Paper, used by everyone, everywhere across all ages, classes, and professions. From the books we read and write to the packaging that protects our food and products, paper remains an important part of modern life. Still, this essential material comes with a hidden environmental cost. The pulp and paper industry is the fifth largest consumer of energy, accounting for 4% of all the world’s energy use.
According to some recent studies, it accounts for approximately 2% of global industrial emissions. Though the use of digital media has risen, the demand for paper continues to grow, putting strain on both the environment and the communities near production facilities.
In today’s world, sustainability and regulatory compliance have become critical priorities for industries. Real-time air quality monitoring technologies like Oizom’s environment monitoring solutions empower paper mills to detect pollutants early, optimize processes, and reduce emissions, helping create cleaner and greener production without compromising output.
Manufacturing Process
The pulp and paper industry typically involves multiple processes transforming wood into finished paper products. While this is essential for contemporary life, each of these steps contributes to air pollution in different ways.
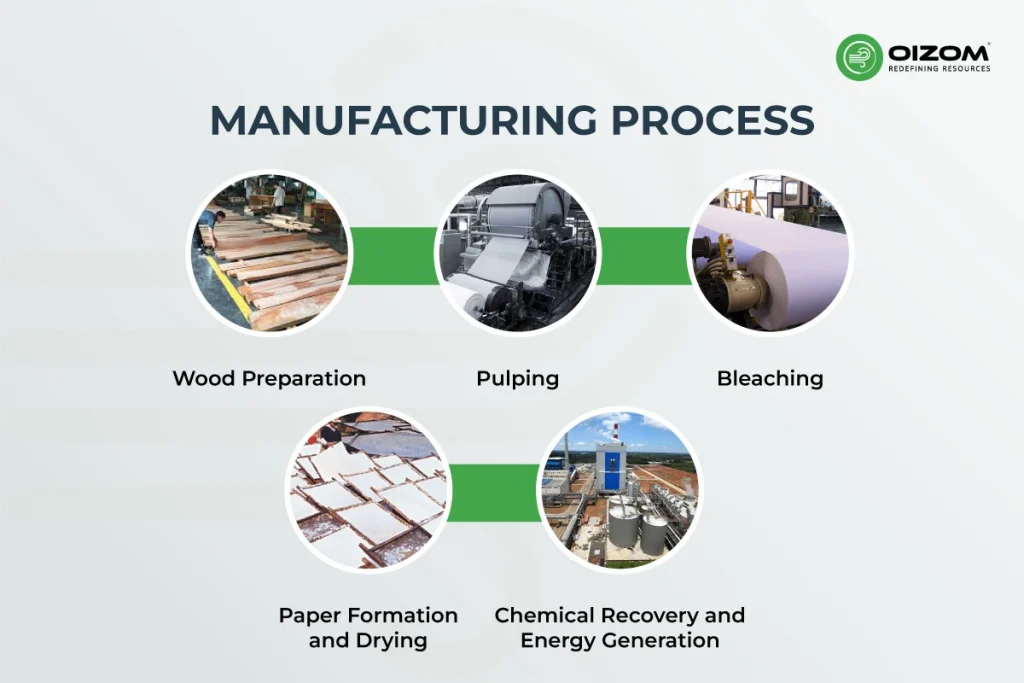
1. Wood Preparation
The first step involves removing barks from logs, which are then chipped into small pieces to prepare them for pulping.
Impact on Air: This step generates a lot of dust and particulate matter (PM) from mechanical handling and wood processing.
2. Pulping
This is where wood chips are converted into the raw material for paper, also called pulp. This can either be done chemically or mechanically:
Chemical Pulping (e.g., kraft process): It uses chemicals to break down lignin and separate fibers used for making paper.
Impact on Air: This method releases sulphur compounds like H₂S and SO₂, along with volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can harm both humans and the environment.
Mechanical Pulping: Here the materials are broken down into pulp instead of using chemicals.
Impact on Air: This method leads to less chemical usage but still results in heat, dust, and CO₂ due to high energy use.
3. Bleaching
The pulp is usually brown due to natural wood compounds like lignin, so it’s bleached to make it white, to improve the paper’s appearance, readability, and print quality.
Impact on Air: Releases VOCs and chlorinated gases, along with strong odors that can affect both workers and nearby communities.
4. Paper Formation and Drying
The pulp is then diluted with water and spread into thin sheets, then pressed and passed through heated rollers to make paper.
Impact on Air: This step requires high energy, leading to CO₂ and NOₓ emissions from fuel combustion during drying.
5. Chemical Recovery and Energy Generation
Black liquor (a byproduct of chemical pulping) is burned to recover chemicals and produce energy.
Impact on Air: This is one of the most polluting stages, emitting high levels of SO₂, NOₓ, PM, and greenhouse gases like CO₂.
Key Air Pollutants in the Pulp & Paper Industry
1. Particulate Matter (PM₁₀, PM₂.₅)
Source:
- Boilers used for steam(energy) generation
- Debarking and chipping of wood
- Burning of biomass or black liquor
- Fly ash from recovery furnaces where black liquor is burned to generate energy and recover chemicals.
2. Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂)
Source:
- SO₂ is released as gas from Recovery boilers
- Fuel combustion
- SO₂ is released when sulphite based chemicals break down wood, also known as sulfite pulping.
3. Sulfur Gases
Source:
- The Kraft pulping process uses chemicals to break down wood and separate fibers to make paper
- Some sulfur gases are emitted during digestion of wood chips with white liquor and also from chemical recovery systems
4. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Source:
- Pulping and bleaching from chemical reactions
- Storage tanks and chemical handling areas
5. Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ)
Source:
- Fossil-fuel boilers used in drying and steam generation
- Lime kilns
6. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Source:
- Fuel combustion and on-site power plants result in CO₂ combustion.
- Transportation and material handling equipment (trucks, loaders) burn fossil fuel, releasing CO₂
7. Odorous Gases
Source:
Odors mainly arise from Kraft pulping (TRS gases) and chlorinated bleaching, impacting air quality and public perception.
Sources of Pollution in the Process Chain
1. Wood Preparation
Logs are shaved and chipped into small pieces. Leading to PM₁₀, PM₂.₅ and wood dust
2. Pulping
Wood chips are converted into pulp through chemical or mechanical processes.
It releases pollutants such as H₂S, SO₂, VOCs, Particulate matter, and CO₂.
3. Bleaching
Pulp, which is usually brown, is whitened using bleaching agents like chlorine dioxide.
This induces pollutants such as Chlorinated VOCs, Odorous gases, and Acid mist
4. Paper Formation & Drying
The whitened pulp is pressed and dried into sheets using heat and rollers.
This results in pollutants such as Carbon dioxide (CO₂), Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), Heat emissions/steam
5. Chemical Recovery & Energy Generation
Black liquor is burned to recover chemicals and generate energy. During recovery, black liquor is burned, which releases Sulfur dioxide (SO₂), Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), Particulate Matter (PM), Carbon dioxide (CO₂), Fly ash, and combustion fumes.
Odour Pollution
Odour is a major concern for pulp and paper mills, especially for nearby communities. These odours primarily come from two key steps:
1. Pulping (Kraft Process)
This stage uses chemicals to break down wood, which releases a pungent smell of sulfur compounds into the air.
Odorous gases include:
- Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), Methyl mercaptan, Dimethyl sulfide, Dimethyl disulfide (TRS) compounds, which are responsible for the “rotten egg” smell around mills.
2. Bleaching
Chlorine-based agents used for bleaching produce a pungent smell.
Odorous emissions include those of Chlorinated VOCs, Acid mist and fumes.
How to Reduce Air Pollution in the Pulp & Paper Industry?

1.Setup & Maintain Air Pollution Control Equipment
Wet scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), and bag filters are devices that can help capture harmful emissions such as particulate matter, SO₂, and acid mist from various units.
However, proper maintenance is very important, defective or uncalibrated equipment often leads to excess emissions and non-compliance.
2.Switching to Cleaner Fuels and Renewable Energy
Replacing fossil fuels with natural gas, biomass, or renewable energy helps reduce CO₂, SO₂, and NOₓ emissions. Also, high-efficiency boilers can help in pollution reduction during drying and steam generation.
3.Adopting Cleaner Pulping & Bleaching Technologies
Use enzymatic pre-bleaching (e.g., xylanase) and chlorine-free bleaching methods instead of chlorine-based agents, which can greatly reduce TRS odours, VOCs, and chlorinated pollutants.
4.Monitoring Emissions Continuously
Deploying continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS) and ambient air quality monitors like Oizom’s Polludrone or Odosense to track real-time SO₂, NOₓ, PM, and VOCs levels.
This can help in early detection, regulatory compliance, and data-based solutions.
5.Promote Sustainable Paper Alternatives
Reducing demand for conventional paper directly reduces pollution from the very start. This can be done by encouraging the use of recycled paper, Tree-free options (e.g., bamboo, bagasse, hemp), Digital workflows Stone paper
How can Oizom help?
Air pollution in the pulp and paper sector is often linked to emissions of hydrogen sulphide (H₂S), particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds — especially during chemical processing and waste handling.
Oizom offers a range of solutions, like the AQBot for specific targeted gas detection, and Odosense for odour-based monitoring across the plant. These devices can be integrated with existing SCADA or DCS systems, enabling automated responses and preventive action.
In one such case, Seshasayee Paper and Boards Ltd (SPB), faced internal complaints due to a 10 ppm H₂S leak near its FRP evaporator. With AQBot deployed and linked to their control system, SPB now receives real-time alerts that safeguard workers and reduce operational risks. (Read the full case insight here.)
Conclusion
Air pollution from the pulp and paper industry stems from multiple stages like pulping, bleaching, drying, and chemical recovery. With a growing demand for paper, the pressure on its impact on the environment is increasing. However, this problem is not short of solutions.
From adopting cleaner fuels and non-chlorine-based bleaching to maintaining effective air pollution control equipment, the industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. Proactive steps are also encouraged through cleaner production and waste utilization. Transitioning to eco-friendly alternatives and promoting digital workflows can also help reduce the demand for traditional paper.
Real-time monitoring plays a crucial role in identifying emission hotspots and ensuring regulatory compliance. Oizom’s advanced solutions such as Dustroid for particulate matter, Odosense for odour monitoring, and Polludrone for overall ambient air quality can help industries identify potential spots and data to take mitigative actions.